This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
A SCAG algorithm for accurate branch detection and angle calculation in soybeans using liDAR data
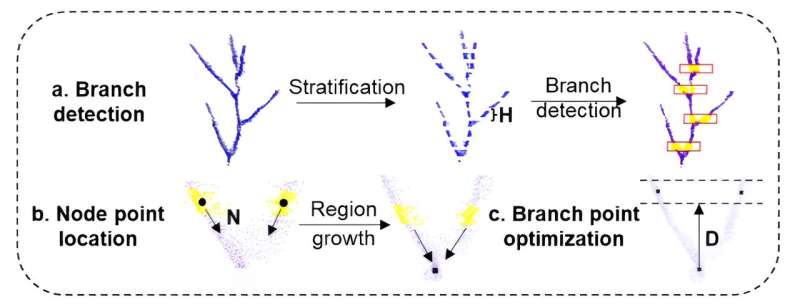
A research team has developed the SCAG algorithm for accurate branch detection and angle calculation in soybean plants using LiDAR data. SCAG achieved high accuracy in branch detection (F-score=0.77) and angle calculation (r=0.84), outperforming traditional methods.
This algorithm identified novel, heritable traits for evaluating soybean density tolerance, such as the average angle to height ratio (AHR) and the angle to stem length ratio (ALR). The open-source SCAG can be applied to other crops, enhancing plant architecture characterization and aiding in ideal variety selection for improved agricultural outcomes.
Soybean is a major source of plant oil and protein, crucial for meeting the demands of a growing global population. Increasing soybean productivity is a long-term breeding goal, but limited arable land and various stresses, particularly nutrient stress, pose challenges. Traditional stress monitoring methods are labor-intensive and inefficient, whereas remote sensing techniques have their own limitations.
Current research highlights the potential of deep learning, particularly Transformer architecture, to enhance hyperspectral imaging analysis. However, combining deep learning with hyperspectral imaging for identifying soybean nutrient stress remains underexplored, which necessitates further investigation.
A study published in Plant Phenomics on 19 May 2024, introduces the SCAG algorithm for accurate branch detection and angle calculation in soybeans using LiDAR data.
This innovative method demonstrated high accuracy in branch detection (F-score=0.77) and angle calculation (r=0.84) when evaluated on 152 diverse soybean varieties, significantly outperforming the SVM (F-score=0.53) and density-based (F-score=0.55) methods. SCAG's robustness was confirmed through parameter sensitivity analysis, showing insensitivity to parameters N and D, and minor sensitivity to parameter H, which should be set to approximately twice the branch diameter for optimal results.
SCAG's applicability was tested on maize and tomato point clouds from the Pheno4D dataset, demonstrating high accuracy in leaf/branch angle calculations (r=0.95 for maize, r=0.94 for tomato), showcasing its potential for diverse crop types. The algorithm also identified novel traits for evaluating soybean density tolerance, such as the average angle to height (AHR) and the ratio of average angle to stem length (ALR), which exhibited better heritability and repeatability compared to traditional traits like the canopy width to height ratio (CHR).
Despite its success, SCAG faces challenges with complex 3D structures, sparse point clouds, and small targets. Future research should focus on improving data quality, addressing missing data issues, and integrating advanced deep learning methods to enhance detection accuracy.
According to the study's lead researcher, Shichao Jin, "Ourwork demonstrates significant advances in 3D phenotyping and plant architecturescreening. The algorithm can be applied to other crops, such as maize and tomato. Ourdataset, scripts, and software are public, which can further benefit the plant sciencecommunity by enhancing plant architecture characterization and facilitating ideal variety selection."
In summary, the open-source SCAG algorithm offers significant potential for enhancing crop development and agricultural productivity. Future research will focus on improving data quality and integrating advanced methods to further expand its applicability.
More information: Shichao Jin et al, SCAG: A stratified, clustered, and growing-based algorithm for soybean branch angle extraction and ideal plant architecture evaluation, Plant Phenomics (2024). DOI: 10.34133/plantphenomics.0190
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences