This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Escaping kinetic traps: How molecular interactions make it possible to overcome the energy barrier
In a paper in Physical Review Letters scientists from the department Living Matter Physics at the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) propose a mechanism on how energy barriers in complex systems can be overcome. These findings can help to engineer molecular machines and to understand the self-organization of active matter.
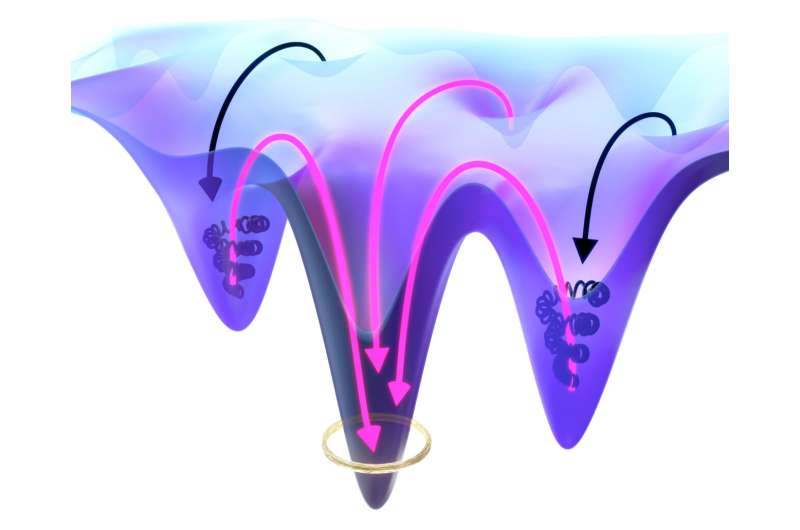
In both physics and biology, systems aim to achieve a state of minimum energy: when a ball rolls down a ramp and over an uneven sandy surface, it eventually comes to a stop in a hollow. Without adding more energy from the outside, it will not start moving again, even if there is a slope or deeper hollow close by to lower the energy level even further.
In biology, this phenomenon is also known from protein folding. Especially in complex systems, proteins might fall into a local energy minimum before completing their assembly. This hampers their function and causes them to be trapped in a static equilibrium state from which they cannot escape.
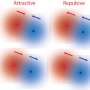
Researchers from MPI-DS have now investigated how non-reciprocal interactions can help to overcome such states. These interactions commonly occur between molecular structures and resemble predator-prey behavior.
One molecule can be attracted by another one, whereas in turn the other one is repelled by the first. This leads to a dynamic interaction which can cause the formation of structures and patterns, as reported before.
"We found that non-reciprocal interactions in active matter can help to overcome energy barriers in these systems," reports Jakob Metson, who is a joint first author of the study, together with Saeed Osat.
In their paper, the scientists propose a generic mechanism using non-reciprocal dynamic interactions to counteract a static equilibrium trap. Their insights can also help to engineer more efficient molecular systems.
"At a conceptual level, our proposed mechanism can achieve what biological enzymes can do, after having been optimized over 3.5 billion years of evolution," says Ramin Golestanian, director of the department Living Matter Physics at MPI-DS.
More information: Saeed Osat et al, Escaping Kinetic Traps Using Nonreciprocal Interactions, Physical Review Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.028301
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by Max Planck Society