This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Researchers develop rechargeable carbonaceous geosupercapacitor for sustainable pollutant abatement

A research team recently developed a sustainable and chemical-free superoxide (O2•−) generation strategy by integrating rechargeable carbonaceous supercapacitors with redox-moiety based O2 activation. These findings have the potential to provide a new strategy for the sustainable remediation of natural water and soil environments. The scientists reported their results in the journal Nature Water.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) enable efficient oxidative removal or detoxification of pollutants in water. However, traditional approaches, such as Fenton or Fenton-like reactions, for ROS generation require large amounts of chemical input, which limits their practical applications.
Direct activation of oxygen (O2) to generate superoxide (O2•−) radicals and their derived ROS are considered as a potential green remediation strategy. Because O2 can be directly obtained from the atmosphere, it avoids the consumption of a large amount of chemicals. However, its yield is constrained by both catalytic materials and electron donors.
To overcome current limitations, "we propose a new strategy for activating molecular oxygen based on rechargeable carbonaceous supercapacitors," said Professor Fangbai Li, in the Institute of Eco-Environmental and Soil Sciences, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, who led the research team.
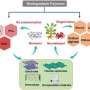
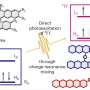
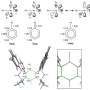
"Highly porous carbonaceous geo-supercapacitors were developed by pyrolyzing waste cattle bones consisting of macromolecules interlinked with abundant minerals."
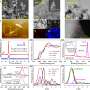
The research team reveals that the developed carbonaceous geo-supercapacitors contain abundant carbon defects and redox-active quinone moieties, thereby effectively transferring electrons to O2 to form O2•−radicals. More importantly, carbonaceous geo-supercapacitors possess excellent electron rechargeability and a stable capacitance, enabling sustainable O2•− production.
This strategy achieves oxidative detoxification transformation of multiple pollutants in different scenarios. It is expected to provide a new strategy for the sustainable remediation of natural water and soil environments.
More information: Liping Fang et al, Rechargeable carbonaceous geosupercapacitor for sustainable superoxide generation and pollutant abatement, Nature Water (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44221-024-00241-6
Journal information: Nature Water
Provided by Institute of Eco-environmental and Soil Sciences, Guangdong Academy of Sciences