This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Team reports on the occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes in the western Qinghai Lake basin
Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) have been widely detected in water, sediment, gut and even the phycosphere of algae. In strong anthropogenic activity areas, antibiotic resistance caused by ARGs can pose a significant threat to human health. Despite the numerous published studies on the occurrence and distribution of ARGs in these areas, there is a dearth of literature on the presence and dispersal of ARGs in remote and pristine environments with limited antibiotic usage.
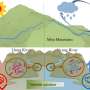
Qinghai Lake, located in the northeastern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, is the largest saltwater lake in mainland China. Notably, it is an important water body for maintaining ecological security. The typical geographical and humanistic features of the Qinghai Lake basin, especially in the northern region, are high altitude (more than 3,000 m), oxygen-deficient environment, low temperature, and sparse human population. Due to governmental protection and national nature reserve policies, the Qinghai Lake basin is less affected by anthropogenic activity.
Nevertheless, it must be acknowledged that the Qinghai Lake basin is a closed watershed with no river outflow. As such, the lake can easily become a sink of ARGs from the watershed and surrounding rivers. In light of this unique geographical background, no prior investigations have explored the occurrence and transmission of ARGs under varied nutrient conditions within the Qinghai Lake basin.
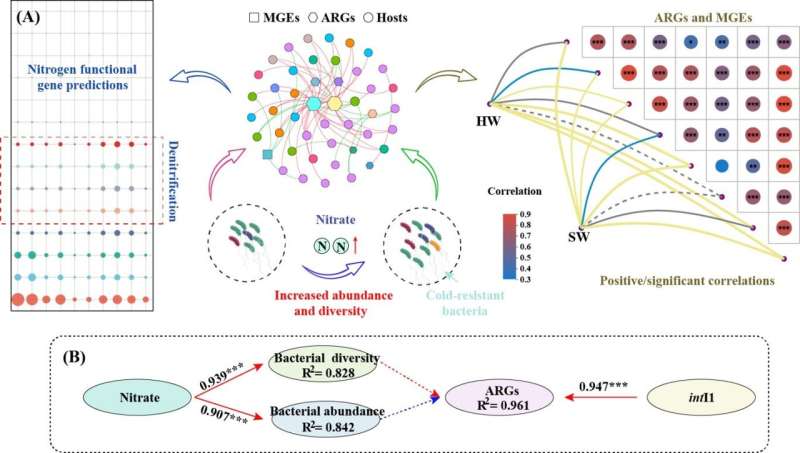
To that end, a team of researchers in China has investigated the microbial community and ARGs in two typical rivers of the western Qinghai Lake basin. The team's findings are published in the journal Water Biology and Security.
"We found that the microbial community was unique in the western Qinghai Lake basin," notes Chenxi Wu, corresponding author of the study. "Specifically, cold-resistant Planomicrobium sp. was the predominant genus due to the low temperature."
Furthermore, the team noted that although ARGs in the western Qinghai Lake basin were significantly lower than that in strong anthropogenic activity areas, a strong correlation between ARGs and intI1 indicated the potential rapid proliferation and spread of ARGs through cross- or co-selection if antibiotic pollution occurs in that area.
The team's findings emphasize the adaptation of bacteria to the environment and the facilitation of anthropogenic activity in the propagation of ARGs in natural environments.
More information: Jia Jia et al, Characteristics of microbial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in typical rivers of the western Qinghai Lake basin, Water Biology and Security (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.watbs.2024.100249
Provided by KeAi Communications Co.