This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Cladophora in Qinghai Lake as an ecological engineer helps increase phytoplankton biodiversity
Excessive filamentous algae growth has become a global concern, posing serious challenges to the management of major bodies of water, including China's Qinghai Lake, the largest lake of Qinghai-Tibet plateau. While many studies have focused on micro-algal blooms, there remains limited research on filamentous algal blooms (FABs).
Cladophora, a filamentous green algae that is widely distributed in both marine and freshwater habitats, has been found to support large, diverse populations of microalgal and bacterial epiphytes that influence the cycling of carbon and other key elements. As such, it has been commonly referred to as an "ecological engineer."
Many highland lakes, such as Qinghai Lake, are generally considered oligotrophic, characterized by low phytoplankton abundance, and with a stable zooplankton and benthic community structure. However, due to an increase in water levels caused by a warmer and moister climate, the newly inundated littoral zone has provided a suitable substrate for the growth of Cladophora.
Furthermore, an abundance of bird droppings near Bird Island provides phosphorus for growth. This has led to a recurrence of Cladophora blooms after a hiatus of nearly half a century. To date, however, the impact of Cladophora meadows on phytoplankton is still unclear, particularly in the context of alpine lakes.
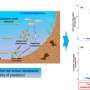
To that end, a team of researchers in China profiled the phytoplankton communities in different regions of Qinghai Lake in different seasons using meta-barcode sequencing.
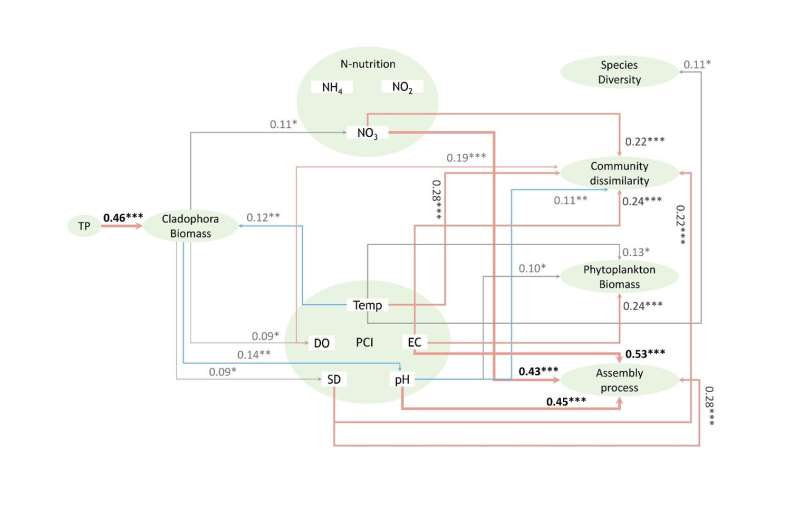
"We compared the phytoplankton assemblages in areas with Cladophora blooms to those without," shared Zhihua Wu, lead author of the study. "We found a correlation between the phytoplankton community structure and various physicochemical factors, including water temperature, electrical conductivity, nitrate levels, and the presence or absence of Cladophora bloom."
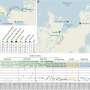
The study identified a greater relative abundance of Bacillariophytes in areas with Cladophora blooms compared to other regions. Additionally, these Cladophora bloom zones showed seasonal fluctuations in phytoplankton biomass and β diversity.
Based on their findings, which were published in Water Biology and Security, the team hypothesized that FABs in alpine lake ecosystems may influence phytoplankton communities.
"FABs can alter the assemblage and assembly process by providing more microhabitats for algae. They could also lead to shifts in the nitrogen level particularly nitrate, possibly through interactions with other nitrogen-fixing organisms," said Wu. "The presence of FABs and its degradation may lead to changes in physicochemical properties, particularly pH, dissolved oxygen and suspended solids which, in turn, can affect the structure of the phytoplankton community."
More information: Zhihua Wu et al, Cladophora as ecological engineer: A new test from the largest lake of Qinghai-Tibet plateau with filamentous algal blooms, Water Biology and Security (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.watbs.2023.100210
Provided by KeAi Communications Co.