This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Brighter, cheaper blue light could revolutionize screen technology
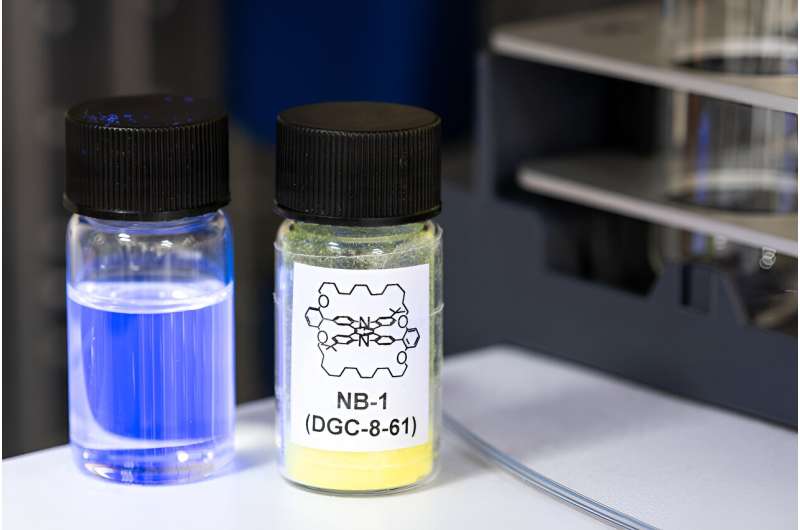

Researchers have found a new way to simplify the structure of high-efficiency blue organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), which could lead to longer-lasting and higher definition television screens.
OLEDs are a class of organic electronics that are already found commercially in smartphones and displays and can be more efficient than competing technologies.
Although OLED television screens have vivid picture quality, they also have drawbacks such as high cost and comparatively short lifespans.
In OLED displays, screen pixels are composed of three different colored subpixels—red, green and blue—that light up at different intensities to create different colors. However, the subpixels that emit blue light are the least stable and can be susceptible to screen "burn-in," which can discolor the screen and ruin viewing quality.
In a paper published in Nature Materials, a team of researchers from Northumbria, Cambridge, Imperial and Loughborough universities describe a new design that overcomes these issues and may lead to simpler, less expensive systems with purer and more stable blue light.
Their findings could lead to TV and smartphone screens using less energy in future, making them more efficient and sustainable.
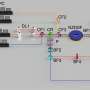
An OLED is built like a sandwich, with organic semiconductor layers between two electrodes. In the middle of the stack is the emissive layer, which lights up when powered with electricity. Electrical energy goes into the molecules, which then release this extra energy as light.
An ideal OLED turns most of the electrical energy into light, but sometimes the energy gets diverted and degrades the structure of the OLED. This is especially a problem with blue light and reduces both the OLED efficiency and lifetime.
Dr. Marc Etherington, Assistant Professor in Molecular Photophysics in Northumbria University's Department of Mathematics, Physics and Electrical Engineering, researches the properties of organic semiconductors.
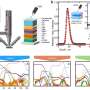
He led a spectroscopic analysis of the triplet energies of the molecules to measure and gain a crucial understanding of how their energy transfer process works.
Dr. Etherington's findings provide a key element to this study, helping the research team form a complete picture of the energy level arrangement.
The research team designed a new light-emitting molecule that has shields added to block the destructive energy pathways and control how the molecules interact.
This better understanding of how efficient a molecule in an OLED can be will inform how materials are designed and used in future, supporting the push towards higher device performance.
Dr. Etherington explained, "With this new molecule we have created a channel to develop more efficient OLEDs that will drive down the energy consumption of our devices in the information era. As we all work towards net zero targets, this could have a significant impact for both manufacturers and consumers."
Co-corresponding author Dr. Daniel Congrave, from the University of Cambridge, who led the material design and synthetic work alongside Prof. Hugo Bronstein, said, "OLED screens have great picture quality and carry a high premium. However, OLED TVs don't last as long as other screens.
"Pixels that emit blue light are essential for a practical display but are also where the problems lie. We've designed a molecule that's allowed us to simplify the emissive layer of the blue pixel to only two components, while maintaining high efficiency, which could help to drive down cost.
"The molecule we describe in this paper is also one of the narrowest emitting blue molecules out there, which is very useful for screens because it allows for high color purity."
More information: Hwan-Hee Cho et al, Suppression of Dexter transfer by covalent encapsulation for efficient matrix-free narrowband deep blue hyperfluorescent OLEDs, Nature Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41563-024-01812-4
Journal information: Nature Materials
Provided by Northumbria University