This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
proofread
New unified theory shows how past landscapes drove the evolution of Earth's rich diversity of life
Earth's surface is the living skin of our planet—it connects the physical, chemical and biological systems.
Over geological time, this surface evolves. Rivers fragment the landscape into an environmentally diverse range of habitats. These rivers also transfer sediments from the mountains to the continental plains and ultimately the oceans.
The idea that landscapes have influenced the trajectory of life on our planet has a long history, dating back to the early 19th century scientific narratives of German polymath Alexander von Humboldt. While we've learnt more since then, many aspects of biodiversity evolution remain enigmatic. For example, it's still unclear why there is a 100-million-year gap between the explosion of marine life and the development of plants on continents.
In research published in Nature today, we propose a new theory that relates the evolution of biodiversity over the past 540 million years to sediment "pulses" controlled by past landscapes.
10 years of computational time
Our simulations are based on an open-source code released as part of a Science paper published earlier this year.
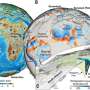
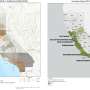
To drive the evolution of the landscape through space and time in our computer model, we used a series of reconstructions for what the climate and tectonics were like in the past.
We then compared the results of our global simulations with reconstructions of marine and continental biodiversity over the past 540 million years.
To perform our computer simulations, we took advantage of Australia's National Computational Infrastructure running on several hundreds of processors. The combined simulations presented in our study are equivalent to ten years of computational time.
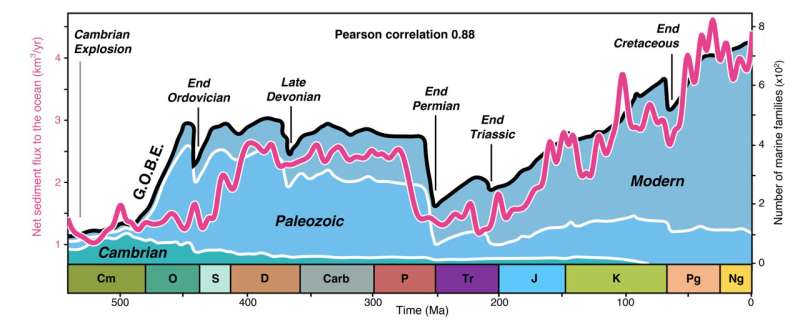
Marine life and river sediment were closely linked
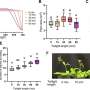
In our model, we discovered that the more sediment rivers carried into the oceans, the more the sea life diversified (a positive correlation). You can see this tracked by the red line in the chart below.
As the continents weather, rivers don't just carry sediment into the oceans, they also bring a large quantity of nutrients. These nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, are essential to the biological cycles that move vital elements through all living things.
This is why we think rivers delivering more or less nutrients to the ocean—on a geological timescale of millions of years—is related to the diversification of marine life.
Perhaps even more surprisingly, we found that episodes of mass extinctions in the oceans happened shortly after significant decreases in sedimentary flow. This suggests that a lack or deficiency of nutrients can destabilize biodiversity and make it vulnerable to catastrophic events (like asteroid impacts or volcanic eruptions).
Landscapes also drove the diversity of plants
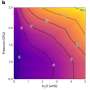
On the continents, we designed a variable that integrates sediment cover and landscape ruggedness to describe the continents' capacity to host diverse species.
Here we also found a striking correlation (see below) between our variable and plant diversification for the past 400 million years. This highlights how changes in landscape also have a strong influence on species diversifying on land.
We hypothesize that as Earth's surface was gradually covered with thicker soil, richer in nutrients deposited by rivers, plants could develop and diversify with more elaborate root systems.
As plants slowly expanded across the land, the planet ended up hosting varied environments and habitats with favorable conditions for plant evolution, such as the emergence of flowering plants some 100 million years ago.
A living planet
Overall, our findings suggest the diversity of life on our planet is strongly influenced by landscape dynamics. At any given moment, Earth's landscapes determine the maximum number of different species continents and oceans can support.
This shows it's not just tectonics or climates, but their interactions that determine the long-term evolution of biodiversity. They do this through sediment flows and changes to the landscapes at large.
Our findings also show that biodiversity has always evolved at the pace of plate tectonics. That's a pace incomparably slower than the current rate of extinction caused by human activity.
More information: Tristan Salles et al, Landscape dynamics and the Phanerozoic diversification of the biosphere, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06777-z
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()