This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Novel measurement technique for fluid-mixing phenomena using selective color imaging method
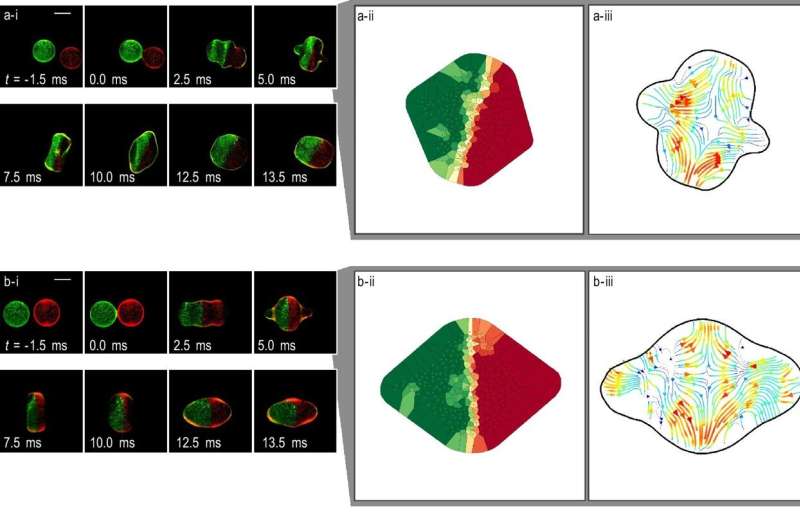
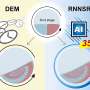
A novel measurement technique has been developed to visualize the fluid flow and distribution within two droplets levitated and coalesced in space using fluorescence-emitting particles. This technique enabled the estimation of fluid motion within each droplet, thereby revealing the internal flow caused by surface vibration when the droplet merging promotes fluid mixing. Details have been published in Scientific Reports.
Generally, handling liquids requires containers. However, ultrasound technology can create a "lab-on-a-drop," an ultracompact testing environment, where multiple liquid droplets of several millimeters in diameter can float and mix in space, without the influence of a container.
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba have developed a technique for merging two droplets, which are challenging to mix due to their small size in this lab-on-a-drop setup, and a method to measure their mixing using a selective color imaging method.
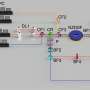
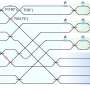
The mixing technique uses an ultrasonic phased array, which creates a focal point where droplets can float randomly via irradiating ultrasonic waves from a 7×7 grid of ultrasonic transducers with phase-shifting. This technique has successfully levitated two identical droplets simultaneously, leading them to collide and merge.
To measure the degree of mixing, it is essential to determine the flow of the fluid within each droplet. Here, the researchers utilized red and green fluorescent emitting particles; one droplet contained particles that fluoresce red under ultraviolet light irradiation, while the other contained particles that fluoresce green.
As the droplets coalesced, the motion of each fluorescent particle was photographed in detail using a high-speed camera, thereby capturing their mixing state.
Based on the time scale required for mixing, a comparative analysis of the difference between fluid mixing due to interfacial vibration during coalescence and due to molecular diffusion revealed that the mixing caused by interfacial vibration was predominant. Therefore, the findings of this research are promising for enhancing the application and further advancement of lab-on-a-drop devices.
More information: Kota Honda et al, Coalescence and mixing dynamics of droplets in acoustic levitation by selective colour imaging and measurement, Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-46008-z
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by University of Tsukuba