This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers develop curated and integrated biomarker knowledgebase for animals
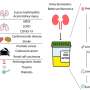
Biological markers, commonly referred to markers or biomarkers, serve as quantifiable and measurable indicators of certain biological states in normal and pathogenic processes, as well as potential pharmacologic responses to therapeutics. They serve as the foundation for diagnostic analysis, the identification of new drug development targets, and the cultivation of new varieties. They play a crucial role in various fields, including personalized medicine, drug development, clinical care, and molecular breeding.
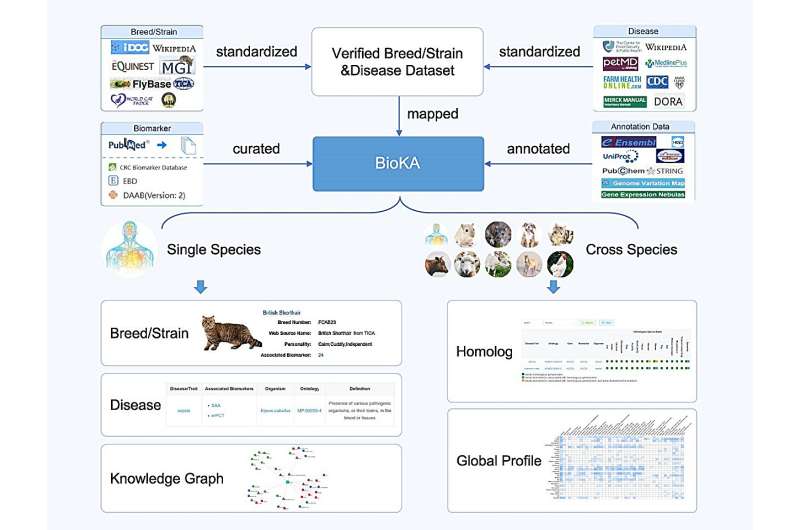
Recently, researchers from Beijing Institute of Genomics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (China National Center for Bioinformation) have developed the Biomarker Knowledgebase for Animals (BioKA), which not only provides rich information on human markers, but also addresses the gap in biomarker resources for non-human animal disease understanding and breeding research. The work was published online in Nucleic Acid Research.
BioKA houses 16,296 biomarkers associated with 951 diseases/traits from a comprehensive compilation of 4,747 literature references across 31 species. Meticulously curated biomarkers include 11,925 gene/protein biomarkers, 1,784 miRNA biomarkers, 1,043 mutation biomarkers, 773 metabolic biomarkers, 357 circRNA biomarkers and 127 lncRNA biomarkers.
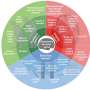
Users can search for specific biomarkers using keywords or gene/protein sequences and access comprehensive annotation information including protein-protein interactions, miRNA targets, variant information, and gene expression data.
Specifically, BioKA focuses on human biomarker research and highlights model animals used for validated biomarkers through various experimental approaches, thus providing traceable support for the reliability of biomarkers. It also provides homologous annotations for 8,784 biomarkers across 16 species, facilitating the discovery of new biomarkers and potential animal models through cross-species comparisons.
In addition, BioKA offers an interactive knowledge graph visualization of biomarkers encompassing 10 species and 7,320 entities, integrating various regulatory relationships including protein-protein interactions, circRNA-miRNA-mRNA interactions, and lncRNA-miRNA associations. This supports the discovery of new biomarkers and facilitates research into associated mechanisms.
The comprehensive knowledge provided by BioKA not only advances human disease research, but also contributes to a deeper understanding of animal diseases and supports livestock breeding.
More information: Yibo Wang et al, BioKA: a curated and integrated biomarker knowledgebase for animals, Nucleic Acids Research (2023). DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad873
Journal information: Nucleic Acids Research , Nucleic Acid Research
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences