October 16, 2023 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Why a spinning magnet can cause a second magnet to levitate
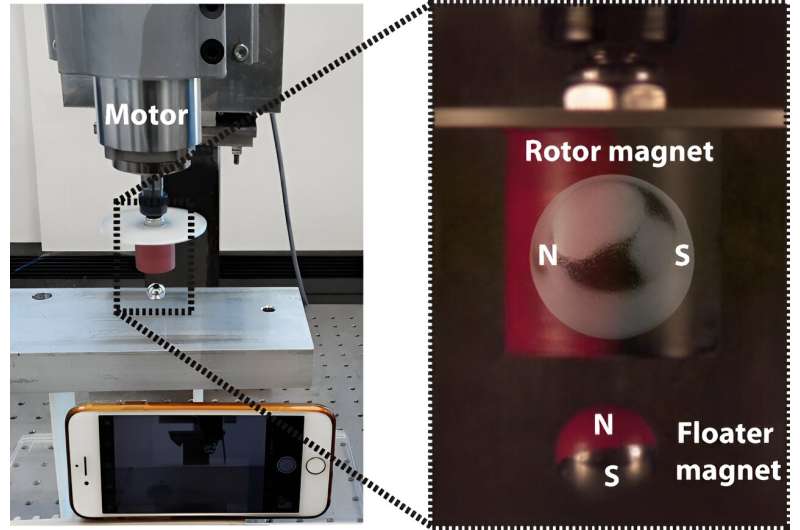
A team of physicists at the Technical University of Denmark has found the reason a spinning magnet can cause a secondary magnet to levitate without the need for stabilization. In their paper published in the journal Physical Review Applied, the group describes experiments they conducted to learn more about the phenomenon and what they learned from them.
Prior research and anecdotal evidence have shown that if two magnets with north poles facing one another are brought close together, they will repel one another. Such force has been used for applications such as levitating trains. But these applications must account for the inherent instability that arises when magnets repel each other.
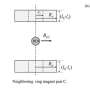
More recently, scientists have found that if one of the magnets is spun at high speed, a second magnet can be repelled without the need for stabilizing—it remains levitated even when the first magnet is moved around. In this new effort, the researchers have uncovered the reason for such behavior.
To learn more about the phenomenon, the research team paired several different types of magnets and spun them at different speeds while recording the action with high-speed cameras and motion tracking software. In studying the resulting imagery, the team was able to uncover the reason for the behavior.
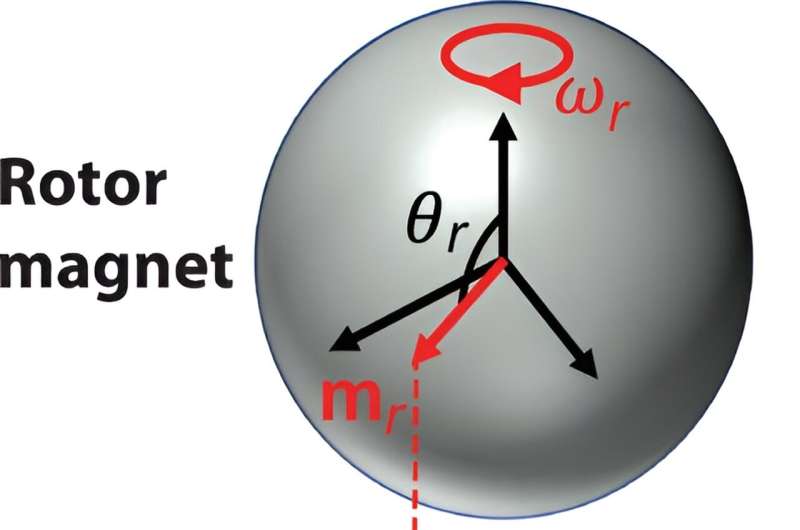
The researchers found that the secondary magnet (which they call a floater) rotated in sync with the rotor magnet—they spun at the same speed. They also found that the axis of the rotor magnet spun with a slight tilt—a situation that would destabilize the two magnets if they were not spinning. To better understand what was happening, the researchers created a simulation that allowed them to more easily manipulate the two magnets and their behavior.
They found that the magnetic field of the rotor magnet exerted some amount of torque on the floater resulting in the two magnets rotating in sync due to a gyroscopic effect. But the floater resisted, if only slightly, which accounted for the parallel configuration that developed. They also found that there was a very small amount of misalignment of the polar axis of the rotor magnet relative to its magnetic field—the resulting attractive and repulsive forces balanced each other out, allowing the floater to be held in a steady position during levitation.
More information: Joachim Marco Hermansen et al, Magnetic levitation by rotation, Physical Review Applied (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.20.044036. On arXiv: doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.00812
Journal information: Physical Review Applied , arXiv
© 2023 Science X Network