This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New species of spiny mouse discovered in rainforest
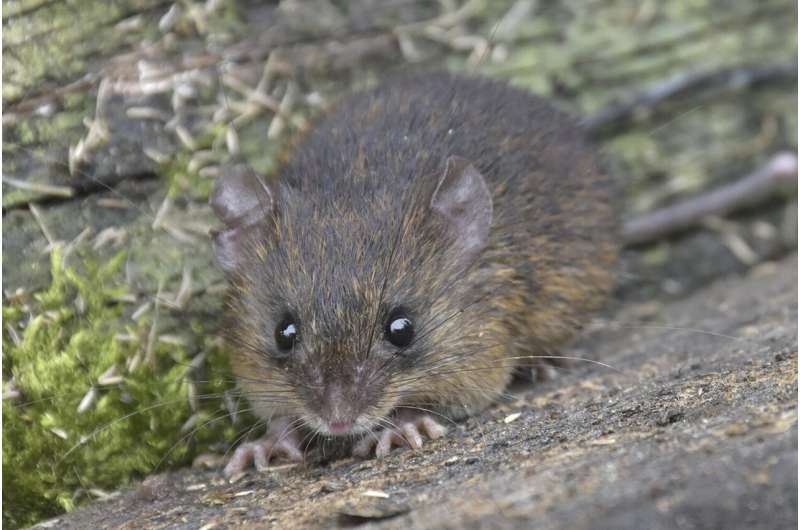

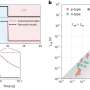
A new species of spiny mouse has been discovered in Ecuador, making it the 14th of its genus to be identified in the past five years. Neacomys marci, which was previously confused with another species, is around the length of a tennis ball, with a long tail, pale suede belly fur and a white throat.
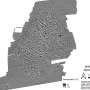
Discovered in the Chocó biogeographic region in northwestern Ecuador, it is the 24th formally recognized species in its genus, which has seen significant upheaval in recent years.
Researchers Nicolás Tinoco, Pontificia Universidad Católica del Ecuador (Quito), Claudia Koch, Leibniz Institute for the Analysis of Biodiversity Change (Germany), Javier E. Colmenares-Pinzón, Universidad Industrial de Santander (Colombia) and Jorge Brito, Instituto Nacional de Biodiversidad (Quito, Ecuador) published their description of the rodent in the open access journal Zookeys.
Neacomys is a widely distributed genus of small spiny or bristly rodents that occupy habitats in eastern Panama and the northern half of South America. Since 2017, studies of the genus have been remarkably dynamic, resulting in the description of several new species.
However, as there are still many unexplored areas in South America and adjacent Central America (Panama), some of the currently recognized species have not been studied thoroughly, and the true diversity of the genus may be underestimated.
The Chocó biogeographic region is considered one of the most diverse biodiversity hotspots in South America, but one of the least studied despite its great size (along the Pacific coasts of Panama, Colombia and Ecuador). The rainforests of northwestern Ecuador have high biodiversity and endemism due to the influence of the Chocó and the Andes Mountains.
Major reviews of museum collections and increased field collection efforts have helped scientists understand Neacomys marci and other species. Molecular analysis is also being used to assist with more accurate animal group identification.
The new species was named after Marc Hoogeslag of Amsterdam, the Netherlands, who was co-founder and leader of the International Union for Conservation of Nature—Netherlands Land Acquisition Fund, which helps local groups around the world establish new ecological reserves and conserve endangered species.
More information: Nicolás Tinoco et al, New species of the Spiny Mouse genus Neacomys (Cricetidae, Sigmodontinae) from northwestern Ecuador, ZooKeys (2023). DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.1175.106113
Journal information: ZooKeys
Provided by Pensoft Publishers