This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Promising quantum state found during error correction research
Window glass, at the microscopic level, shows a strange mix of properties. Like a liquid, its atoms are disordered, but like a solid, its atom are rigid, so a force applied to one atom causes all of them to move.
It's an analogy physicists use to describe a quantum state called a "quantum spin-glass," in which quantum mechanical bits (qubits) in a quantum computer demonstrate both disorder (taking on seemingly random values) and rigidity (when one qubit flips, so do all the others). A team of Cornell researchers unexpectedly discovered the presence of this quantum state while conducting a research project designed to learn more about quantum algorithms and, relatedly, new strategies for error correction in quantum computing.
"Measuring the position of a quantum particle changes its momentum and vice versa. Similarly, for qubits there are quantities which change one another when they are measured. We find that certain random sequences of these incompatible measurements lead to the formation of a quantum spin-glass," said Erich Mueller, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S). "One implication of our work is that some types of information are automatically protected in quantum algorithms which share the features of our model."
"Subsystem Symmetry, Spin-glass Order, and Criticality From Random Measurements in a Two-dimensional Bacon-Shor Circuit" published on July 31 in Physical Review B. The lead author is Vaibhav Sharma, a doctoral student in physics.
Assistant professor of physics Chao-Ming Jian (A&S) is a co-author along with Mueller. All three conduct their research at Cornell's Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics (LASSP).
"We are trying to understand generic features of quantum algorithms—features which transcend any particular algorithm," Sharma said. "Our strategy for revealing these universal features was to study random algorithms. We discovered that certain classes of algorithms lead to hidden 'spin-glass' order. We are now searching for other forms of hidden order and think that this will lead us to a new taxonomy of quantum states."
Random algorithms are those that incorporate a degree of randomness as part of the algorithm—e.g., random numbers to decide what to do next.
Mueller's proposal for the 2021 New Frontier Grant "Autonomous Quantum Subsystem Error Correction" aimed to simplify quantum computer architectures by developing a new strategy to correct for quantum processor errors caused by environmental noise—that is, any factor, such as cosmic rays or magnetic fields, that would interfere with a quantum computer's qubits, corrupting information.
The bits of classical computer systems are protected by error-correcting codes, Mueller said; information is replicated so that if one bit "flips," you can detect it and fix the error. "For quantum computing to be workable now and in the future, we need to come up with ways to protect qubits in the same way."
"The key to error correction is redundancy," Mueller said. "If I send three copies of a bit, you can tell if there is an error by comparing the bits with one another. We borrow language from cryptography for talking about such strategies and refer to the repeated set of bits as a 'codeword.'"
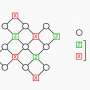
When they made their discovery about spin-glass order, Mueller and his team were looking into a generalization, where multiple codewords are used to represent the same information. For example, in a subsystem code, the bit "1" might be stored in 4 different ways: 111; 100; 101; and 001.
"The extra freedom that one has in quantum subsystem codes simplifies the process of detecting and correcting errors," Mueller said.
The researchers emphasized that they weren't simply trying to generate a better error protection scheme when they began this research. Rather, they were studying random algorithms to learn general properties of all such algorithms.
"Interestingly, we found nontrivial structure," Mueller said. "The most dramatic was the existence of this spin-glass order, which points toward there being some extra hidden information floating around, which should be useable in some way for computing, though we don't know how yet."
More information: Vaibhav Sharma et al, Subsystem symmetry, spin-glass order, and criticality from random measurements in a two-dimensional Bacon-Shor circuit, Physical Review B (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.108.024205
Journal information: Physical Review B
Provided by Cornell University