This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Cars, chlamydia and canines are biggest koala killers
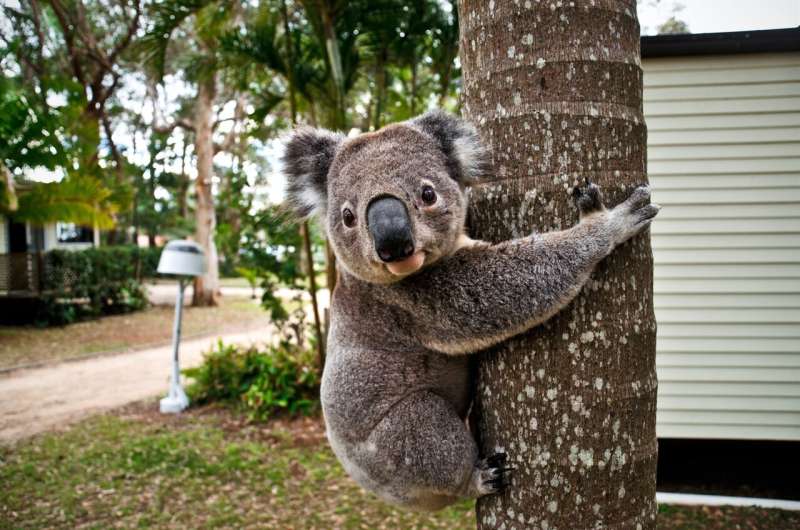

A database tracking hospital admissions and deaths reveals the devastating impact cars, disease and dogs are having on the South East Queensland koala population.
Professor Joerg Henning and his colleagues at The University of Queensland School of Veterinary Science have analyzed data from the UQ-developed KoalaBASE.
"Car strikes, dog attacks and chlamydia-induced illnesses are injuring and killing an incredible number of koalas across the South East Queensland," Professor Henning said.
"In the five years between 2009 and 2014, 52% of reported wild koala deaths were caused by car strike, 34% were from a chlamydia-related disease and 14% were because of a dog attack.
"This equates to 1,431 koala deaths from a car strike, 943 chlamydia-related deaths, and 395 dog attack deaths in just five years.
"Remember that these deaths were just the reported cases, so the real numbers would be significantly higher."
The research has been published in Scientific Reports.
KoalaBASE has been collecting data since 1997 across 15 local government areas from the Fraser Coast, to the Scenic Rim and Darling Downs and the South Burnett.
Dr. Ravi Dissanayake conducted the initial analysis, supervised by UQ colleagues and Professor Mark Stevenson at the University of Melbourne.
Data considered in the analysis included dog registration numbers, the human population and dwelling information, as well as road type and road length.
"This analysis is a useful starting point for more pro-active approaches to managing preventable wild koala mortality risk," Professor Stevenson said.
"There are plenty of policies that could reduce car and dog impacts on South East Queensland's dwindling wild koala populations."
Professor Henning suggests that more road signs could alert motorists to reduce their speed in known koala habitat and activity areas.
"Construction of over and underpasses is also essential to ensure the safe movement of koalas through their habitat," Professor Henning said.
"And information campaigns could help reduce the numbers of dog attacks on koalas by reminding owners to leash their dogs or keep them fenced in areas— it's vitally important to reduce koala deaths caused by dogs.
"Our research included plenty of mapping, so we're now keen to work with policymakers to identify specific areas where intervention efforts can help to reduce koala deaths."
More information: Ravi Bandara Dissanayake et al, Anthropogenic and environmental factors associated with koala deaths due to dog attacks and vehicle collisions in South-East Queensland, Australia, 2009–2013, Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-40827-w
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by University of Queensland