This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Magnetic bacteria provide clues for the early diversification of bacteria
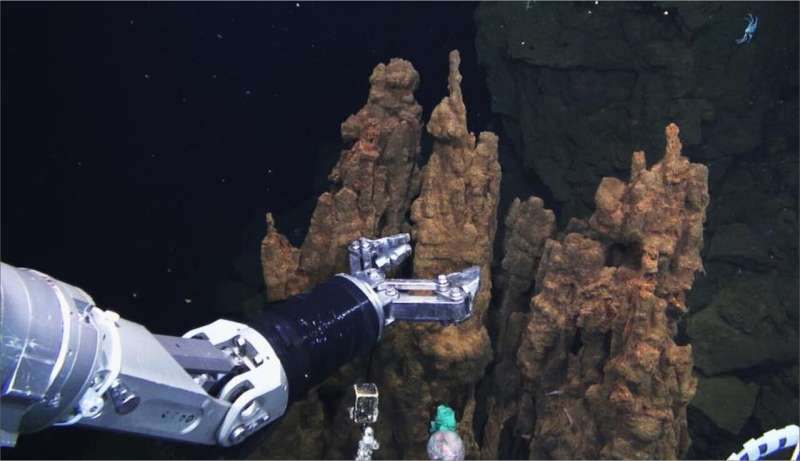

Magnetotactic bacteria, which can align with the Earth's magnetic field, have been discovered in a new location. Previously observed on land and in shallow water, analysis of a hydrothermal vent has proven that they can also survive deep under the ocean. The bacteria were able to exist in an environment that was not ideal for their typical needs. The research has been published in Frontiers in Microbiology.
Magnetotactic bacteria are of interest not only for the role they play in Earth's ecosystem, but also in the search for extraterrestrial life. Evidence of their existence can remain in rocks for billions of years. Their magnetic inclinations can also provide a record of how magnetic poles have shifted over time. This new discovery brings hope to researchers that the magnetic bacteria might be found in yet more unexpected locations, on Earth and perhaps even on Mars or beyond.
Magnetotactic bacteria seem to have superpowers; they can "sense" the Earth's magnetic field. These tiny organisms contain magnetosomes, iron crystals wrapped in a membrane, which arrange themselves to align with the Earth's magnetic field and point the bacteria like a compass. This causes the bacteria to travel in the direction of Earth's magnetic field lines leading north or south, like trains on a magnetic track.
As part of their life cycle, they play an important role in the biogeochemical cycling of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous and other key elements in nature. They have been well studied on land and in shallow water, but rarely in deep water where collecting them can be a challenge.
In September 2012, a team including researchers from the University of Tokyo embarked on a scientific ocean cruise to the southern Mariana Trough in the western Pacific Ocean. Using a remotely operated underwater vehicle named HYPER-DOLPHIN, they collected a "chimney" from a hydrothermal vent field 2,787 meters (almost 4.5 times the height of Tokyo Skytree or more than six times the height of the Empire State Building in New York) underwater.
Hydrothermal vents are formed when seawater percolates down underground, eventually becoming superheated—up to 400° Celsius—by magma which causes it to boil back up. The erupting water deposits minerals and metals into the ocean which layer up to form chimneys, providing a warm, rich habitat for many unique forms of life.
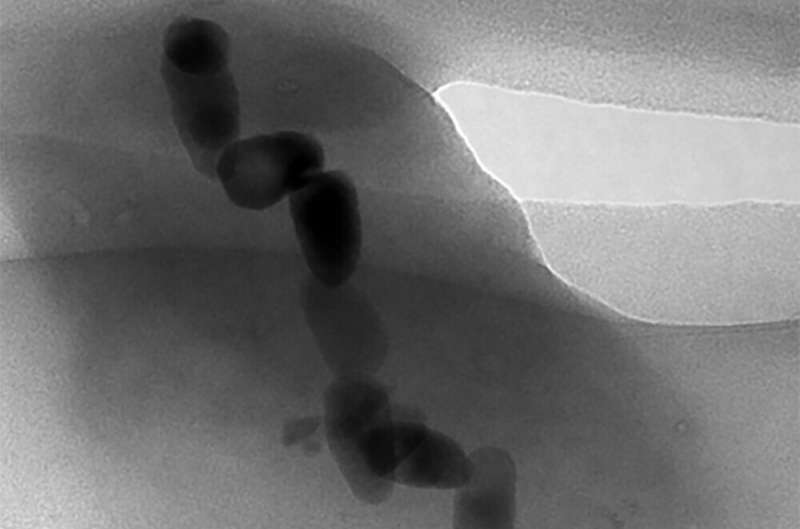
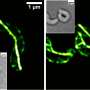
"We discovered magnetotactic bacteria living on the chimney, which we didn't expect. Due to the chimney's shape, it lacks a clear, vertical chemical gradient which these bacteria typically prefer," explained Associate Professor Yohey Suzuki from the Graduate School of Science at the University of Tokyo. "The bacteria we collected contained mainly 'bullet'-shaped magnetosomes, which we see as a 'primitive' form and so inferred that they have not changed much over many millennia. Indeed, the environment we found them in is similar to early Earth about 3.5 billion years ago, when the ancestor of magnetotactic bacteria is estimated to have emerged."
Bacteria were collected from the rim of the chimney using a magnet. The team then examined the genetic data and found that they were related to the bacteria Nitrospinae, which are known to play an important role in carbon fixation in deep-sea environments, but which were not known to contain any magnetotactic groups.
"Deep-sea hydrothermal vents attract attention not only as the birthplace of unique underwater life, but also as a potential analogous habitat for extraterrestrial life," said Suzuki. "The environment where we sampled the bacteria is similar to what we think Mars was like when there was still flowing water on its surface, about 3 billion years ago."
Fossilized remains of the magnetic particles in magnetotactic bacteria (known as magnetofossils) can be preserved in rock for billions of years. These magnetofossils can help researchers piece together ancient geomagnetic history and are good candidates in the search for extraterrestrial life.
In 1996, the Martian meteorite Allan Hills 84001, which is about 3.6 billion years old, caused a global sensation when it appeared to contain iron-crystal fossils from bacteria-like life. The claim has since been widely disputed, but Suzuki still has hope for future discoveries.
"Magnetotactic bacteria provide clues for the early diversification of bacteria and we hope they will be found beyond Earth, maybe on Mars or icy moons. For now, we will continue to look for more evidence of them in various types and ages of rocks on Earth where they were not previously thought to inhabit."
More information: Bullet-shaped magnetosomes and metagenomic-based magnetosome gene profiles in a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney., Frontiers in Microbiology (2023). DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1174899
Journal information: Frontiers in Microbiology
Provided by University of Tokyo