This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Novel computational approach reveals previously inaccessible druggable pockets
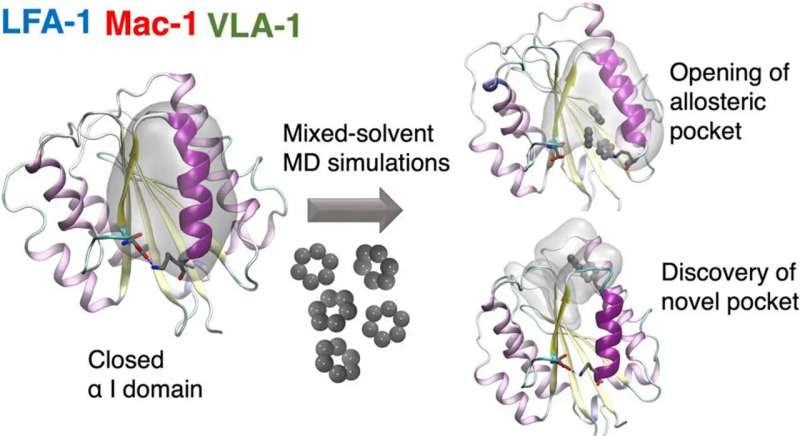
A team of researchers from the Universities of Amsterdam and Zurich together with the Swiss company Allocyte Pharmaceuticals have for the first time been able to discover allosteric sites in a type of cell surface receptor called integrin.
In a paper recently published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, they describe how this reveals previously inaccessible druggable integrin pockets. At the heart of the research is a novel computational approach for mixed-solvent molecular dynamics simulation developed by Dr. Ioana Ilie at the Computational Chemistry group of the Van 't Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences at the University of Amsterdam.
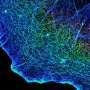
Integrins are a family of cell surface adhesion receptors which are capable of transmitting signals bidirectionally across membranes. They are known for their therapeutic potential in a wide range of diseases. However, the development of integrin targeting medication has been impacted by unexpected downstream effects. In particular, these are observed with drugs targeting the native binding site of the integrin.
The so-called allosteric modulation of integrins is a promising approach to potentially overcome these limitations. Here, the drug binds elsewhere on the receptor, changing the conformation and thus impacting the activity of the protein. Allosteric modulation of receptors therefore creates opportunities for drug discovery and development which are potentially superior to classic orthosteric modulation.
Novel druggable pockets
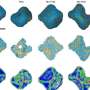
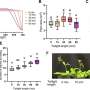
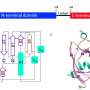
The novel computational approach developed by Ioana Ilie relies on enriching the solvent with small organic molecules (benzene in small concentrations) to enable the gentle opening of the integrin α I domain. This revealed novel previously inaccessible druggable pockets within the integrins LFA-1, VLA-1, and Mac-1. This study thus offers structural and dynamic insight on the effect of small alterations in solvent conditions on the accessibility of novel potentially druggable pockets, which are validated via virtual screening. The study acts as proof of concept and sets the foundation for the design of the next-generation integrin-targeting drugs. Additionally, it opens new research avenues towards the identification of allosteric sites in other up to date undruggable protein targets.
Finally, the study goes beyond drug discovery as it demonstrates that minor changes in the solvent conditions can have a dramatic impact on the conformational space of the solvated molecule. This offers the opportunity to tune the solvent conditions in order to obtain a specific response of the solvated molecule (e.g., protein, material), which implicitly can aid in the development novel bio-inspired materials with responsive properties.
More information: Ioana M. Ilie et al, Decrypting Integrins by Mixed-Solvent Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c00480
Journal information: Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling
Provided by University of Amsterdam