In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which drugs are discovered and/or designed.
In the past most drugs have been discovered either by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery. A new approach has been to understand how disease and infection are controlled at the molecular and physiological level and to target specific entities based on this knowledge.
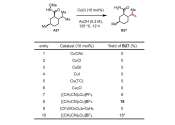
The process of drug discovery involves the identification of candidates, synthesis, characterization, screening, and assays for therapeutic efficacy. Once a compound has shown its value in these tests, it will begin the process of drug development prior to clinical trials.
Despite advances in technology and understanding of biological systems, drug discovery is still a lengthy, "expensive, difficult, and inefficient process" with low rate of new therapeutic discovery. Information on the human genome, its sequence and what it encodes has been hailed as a potential windfall for drug discovery, promising to virtually eliminate the bottleneck in therapeutic targets that has been one limiting factor on the rate of therapeutic discovery.[citation needed] However, data indicates that "new targets" as opposed to "established targets" are more prone to drug discovery project failure in general[citation needed] This data corroborates some thinking underlying a pharmaceutical industry trend beginning at the turn of the twenty-first century and continuing today which finds more risk aversion in target selection among multi-national pharmaceutical companies.[citation needed]