This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Bridging the gap between AI and manual precision in 3D cell segmentation

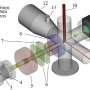
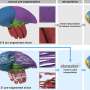
Researchers from Nagoya City University have made an important advancement in the field of cellular imaging with the development of Seg2Link, a software tool that harnesses the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and semi-automated correction techniques to accurately segment cells in 3D images from a stack of 2D images. This solution bridges the gap between AI predictions and real-world accuracy, enabling scientists to process large-scale image data more efficiently. Their paper is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Traditional AI-based methods for cell segmentation have their limitations, mainly due to inaccuracies in the automated detection of cellular regions. To address this, Seg2Link integrates deep learning technology with efficient manual corrections. Users can easily refine the AI-determined cell regions in the first 2D image, and the software will semi-automatically apply these corrections to subsequent 2D slices, dramatically reducing the time and effort required for 3D cell segmentation.
Notably, the software is designed to be user-friendly and can run efficiently on standard personal computers. This means that even non-experts can utilize Seg2Link to process large-scale image data quickly, a significant advantage given the current trend of biological images becoming increasingly large-scale, or "big data."
The implications of this development are wide-reaching, with the potential to catalyze research progress in various fields. In medicine and biology, for instance, efficient processing of biological images could accelerate research into tumor cell proliferation, cancer progression, and treatment effectiveness. The software could also assist in analyzing neural circuits, helping to further understand brain disorders.
More information: Chentao Wen et al, Seg2Link: an efficient and versatile solution for semi-automatic cell segmentation in 3D image stacks, Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-34232-6
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Nagoya City University