This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Scientists create computer simulation based on digital microbes
Researchers at University of Galway associated with APC Microbiome Ireland have created a resource of over 7,000 digital microbes—enabling computer simulations of how drug treatments work and how patients may respond.
The resource is a milestone in scientific understanding of human response to medical treatment as it offers the opportunity for computer simulations and predictions of differences in metabolism between individuals, including for diseases such as inflammatory bowel, Parkinson's and colorectal cancer.
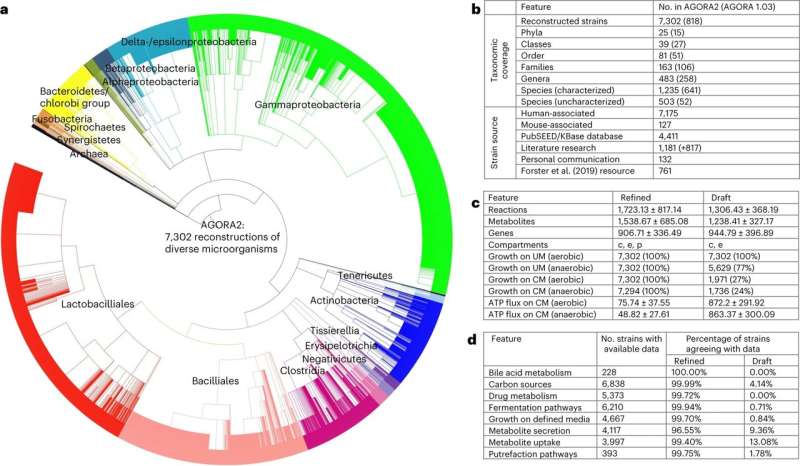
The database—called AGORA2—builds on the expertise developed in the creation of first resource of digital microbes known as AGORA1. AGORA2 encompasses 7,203 digital microbes, created based on experimental knowledge from scientific publications, with a particular focus on drug metabolism.
The resource has been built by a team of scientists at University of Galway's Molecular Systems Physiology group, led by APC Microbiome Ireland principal investigator Professor Ines Thiele.
The team's research aims to advance precision medicine by using computational modeling.
Professor Thiele explained, "AGORA2 is a milestone towards personalized, predictive computer simulations enabling the analysis of person-microbiome-drug interactions for precision medicine applications."
"Humans are hosting a myriad of microbes. Just like us, these microbes eat and interact with their environment. Considering that we are all unique, each of us hosting an individual microbiome our metabolism is also expected to vary between individuals."
"The insight provided by the database of digital microbes presents a healthcare opportunity to harness individual differences in metabolism to provide personalized, improved treatments in 'precision medicine', compared to a currently more general 'one-size-fits-all' approach."
"Besides our food, our individual microbiomes also metabolize the medicines we take. The same drug may therefore manifest diverse effects in disparate people because of the differences in metabolism performed by the different microbiomes."
Using the digital microbe resource AGORA2, computer simulations have shown that drug metabolism varies significantly between individuals, as driven by their own microbiomes.
Uniquely, the AGORA2-based computer simulations enabled the identification of microbes and metabolic processes for individual drugs correlated with observations in a clinical setting.
The research was published today in Nature Biotechnology.
The team at University of Galway demonstrated that AGORA2 enables personalized, strain-resolved modeling by predicting the drug conversion potential of the gut microbiomes from 616 colorectal cancer patients and controls, which greatly varied between individuals and correlated with age, sex, body mass index and disease stages. This means that the team can create digital representations and predictions specific to the divergent microbes.
Professor Thiele added, "Knowledge of our individual microbiomes and their drug metabolizing capabilities represents a precision medicine opportunity to tailor drug treatments to an individual to maximize health benefit while minimizing side effects."
"By using AGORA2 in computer simulations our team have showed that the resulting metabolic predictions enabled superior performance compared to what was possible to date."
Professor Paul Ross, Director of APC Microbiome Ireland, said, "This research is a perfect illustration of the power of computational approaches to enhance our understanding of the role of microbes in health and disease—significantly this digital platform will be a fantastic resource that could lead to the development of novel personalized therapeutic approaches which take the microbiome into account."
More information: Almut Heinken et al, Genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of 7,302 human microorganisms for personalized medicine, Nature Biotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01628-0
Journal information: Nature Biotechnology
Provided by University of Galway