Near-infrared-triggered nanozyme for synergistic cascade tumor therapy
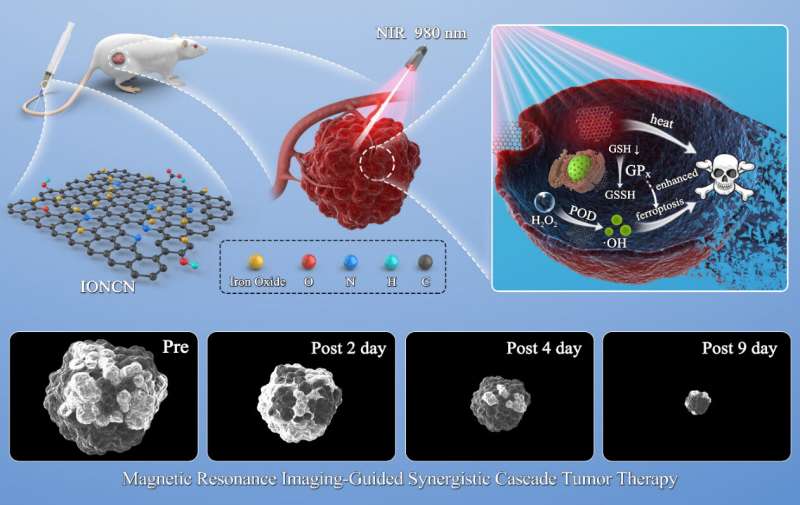
A joint research team led by Prof. Wang Hui, Prof. Zhang Xin and Prof. Qian Junchao from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has proposed a new kind of near-infrared-triggered nanozyme based on iron oxide nanocrystals embedded in N-doped carbon nanosheets (IONCNs), which is promising for synergistic cascade tumor therapy.
The study was published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Chemodynamic therapy is an efficient cancer treatment method determined by the striking difference between the tumor microenvironments and normal tissues. By triggering the Fenton or Fenton-like reaction, it can generate highly toxic hydroxyl radical (·OH) to kill tumor cells.
Unfortunately, the overexpression of glutathione in tumor microenvironments limits the therapeutic efficacy by counteracting ·OH generation. Moreover, the normal cells or inflammatory cells are easily affected simultaneously owing to their similar characteristics to the tumor microenvironments. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an exogenous triggered nanozyme to realize tumor-specific catalytic therapy.
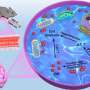
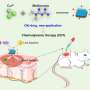
In this study, the researchers used a one-step hydrothermal method to synthesize IONCNs.
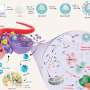
The as-prepared IONCNs could absorb and convert 980 nm light to local heat that not only killed cancer cell by photothermal therapy but also induced the dissolution of iron oxide to produce Fe2+/Fe3+ in a weak acid solution.
The formed Fe2+ catalyzed the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to generate hydroxyl radical for chemodynamic therapy. The formed Fe3+ acted as a glutathione peroxidase to amplify the oxidative stress of cancer cells and therapeutic effect of chemodynamic therapy.
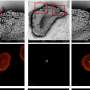
Additionally, the IONCNs could be used as a magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent to visually monitor the treatment process of cancer.
More information: Hongji Liu et al, Exogenously Triggered Nanozyme for Real-Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Synergistic Cascade Tumor Therapy, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c07375
Journal information: ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences