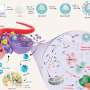
'Nanocapsules' provide new solution for efficient cancer chemodynamic therapy
In a paper published on Small recently, a collaborated research team led by Prof. Wang Hui from High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported the synthesis of hollow cuprous oxide@nitrogen-doped carbon (HCONC) by one-step hydrothermal method as well as their applications in efficient chemodynamic therapy.
In recent years, chemodynamic therapy (CDT) responsive to tumor microenvironment (TME) has received extensive attention due to its low invasiveness and high selectivity. Among various metal-based nanocatalysts, the low redox potential of Cu+/Cu2+ in cuprous-based nanocatalysts endows them with higher reactive oxygen species (ROS) yields and reduced glutathione (GSH) overexpression, which can also be shown great promise as a Fenton-like agent under relatively loose conditions. However, the susceptibility to oxidation and potential ionic toxicity of cuprous-based nanocatalysts severely limit their applications in nanomedicine. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a cuprous-based nanocatalyst with good biocompatibility to deplete the overexpression of GSH to enhance CDT.
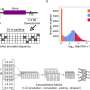
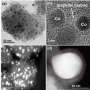
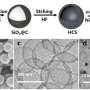
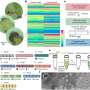
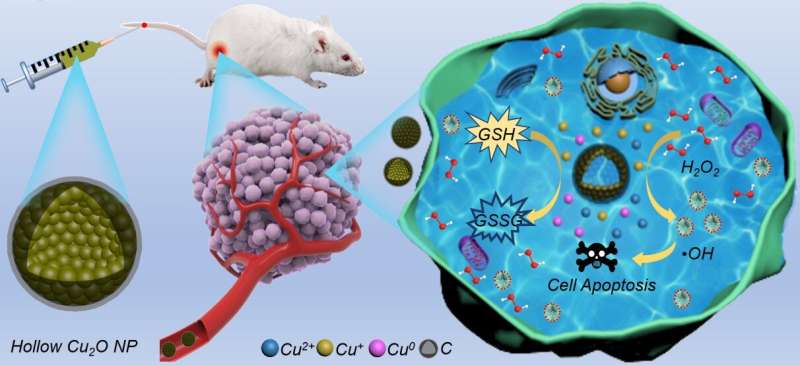
In this research, researchers used a one-step hydrothermal method to synthesize HCONC nanocapsules for catalyzing the cascade reaction and improving the efficacy of CDT. This "nanocapsules" composed of nanoparticles is not "capsules" in the traditional sense. It is a core-shell structure formed by ingeniously attaching a thin layer of carbon to the surface of hollow cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanocrystals, which not only effectively prevents the oxidation of Cu+, but also increases stability of Cu2O nanocrystals.
The Cu+-mediated Fenton-like reaction in HCONC can efficiently catalyze H2O2 to generate ·OH, and the Cu+ released in the TME can also decompose overexpressed GSH to protect nascent ROS.
Both in vitro and in vivo experiments show that HCONC has excellent antitumor ability without causing systemic toxicity. "The whole process can be described in a old saying," added Prof. Wang, "as the medicine took effect, the symptoms lessened."
More information: Xiangfu Meng et al, Hollow Cuprous Oxide@Nitrogen‐Doped Carbon Nanocapsules for Cascade Chemodynamic Therapy, Small (2022). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202107422
Journal information: Small
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences