Research team identifies a molecular code embedded in protein for regulating its glycosylation
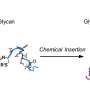
Many proteins in nature exist as glycoproteins, which consist of protein (polypeptide chain) and glycan (sugar chain). The protein structure is determined on the basis of its genetic blueprint, but the information on glycans is not directly encoded by the genome. Therefore, it is difficult to control protein glycosylation.
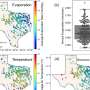
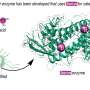
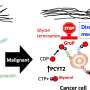
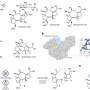
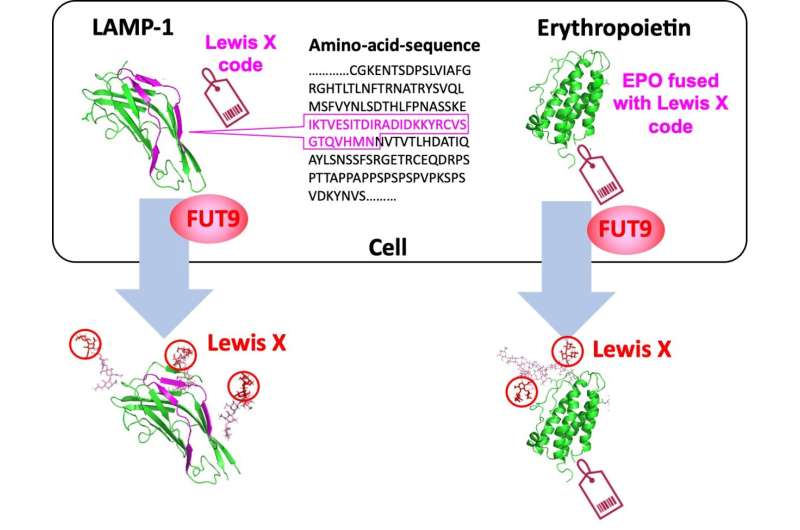
Under these circumstances, a collaborative research group, including researchers at Nagoya City University, National Institutes of Natural Sciences, and Academia Sinica has found a specific amino acid sequence in a polypeptide that induces a specific glycan structure called Lewis X. The researchers in Japan have previously shown that Lewis X specifically modifies the protein LAMP-1 in mouse neural stem cells through the enzymatic action of fucosyltransferase 9 (FUT9).
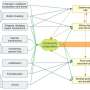
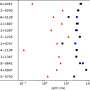
In this most recent study published in Communications Biology, they have shown that Lewis X modification specific for LAMP-1 occurs not only in neural stem cells but also in several cultured mammalian cells. Furthermore, they have found that a sequence consisting of 29-amino-acid residues in LAMP-1 promotes Lewis X modification catalyzed by the enzyme, and this sequence induces Lewis X modification when fused to other proteins used as biopharmaceuticals. This means that in glycoprotein molecules, a specific amino-acid sequence can determine their glycan structures.
Most biopharmaceuticals are glycoproteins, as best exemplified by therapeutic antibodies. Their glycan structures are critical for their efficacy and safety. Therefore, the control of glycosylation is an important issue in the development of biopharmaceuticals. These findings on a regulatory code of protein glycosylation are expected to pave the way for controlling glycosylation of biopharmaceuticals.
More information: An embeddable molecular code for Lewis X modification through interaction with fucosyltransferase 9, Communications Biology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03616-1
Journal information: Communications Biology
Provided by Nagoya City University