Propagation of parasite in toxoplasmosis host cell stopped
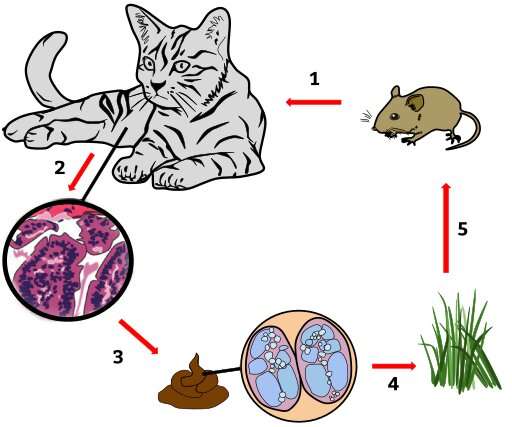
Toxoplasmosis is one of the most widespread zoonoses worldwide. It is an infectious disease that can be transmitted from cats to humans. People can also become infected by consuming raw or undercooked meat. Infection is particularly dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause fetal deformities.
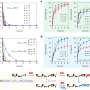
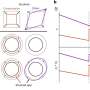
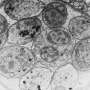
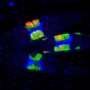
The cause of the disease is the single-celled parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Inside the host cell, it forms a little bubble-like compartment called a parasitophorous vacuole, which facilitates nutrient exchange and synchronized cell division. The resulting daughter cells are connected with each other inside the vacuole via a network, somewhat akin to an umbilical cord. Up to 64 daughter cells can form in the compartment. As soon as the offspring are mature, a regulation mechanism prompts the dissolution of the vacuole and the structures that have formed inside it. This is the moment at which the daughter cells become mobile and invade new host cells.
Hope for the development of new drugs
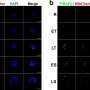
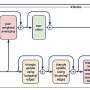
Before now, it was not known which genes encode the proteins that control the exit from the host cell. To identify them, a team led by Prof. Markus Meißner, Chair of Experimental Parasitology at LMU, collaborated with colleagues from the University of Glasgow in Scotland to develop a novel genetic screening technique, which is based on the Cas9 "genetic scissors," and investigate a library of 320 parasite-specific genes. They discovered two genes without which cell egress is impossible.
The targeted destruction of these genes led to a blockade of the egress and thus to the death of the next generation of parasites within the host cell. "This paves the way potentially for the development of active substances that could block the function of the corresponding proteins and so put a halt to propagation," observes Markus Meißner.
Toxoplasma gondii is closely related to the malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum. Therefore, the parasite serves as a model organism for the pathogen of the tropical disease, which kills hundreds of thousands of people worldwide every year. "We assume that similar processes control the propagation of the malaria pathogen," explains LMU parasitologist Dr. Elena Jimenez-Ruiz. "Next, we will investigate what functions these proteins have in the malaria pathogen and whether there are possible starting points for the development of new drugs."
The study appears in Nature Microbiology.
More information: Wei Li et al, A splitCas9 phenotypic screen in Toxoplasma gondii identifies proteins involved in host cell egress and invasion, Nature Microbiology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41564-022-01114-y
Journal information: Nature Microbiology
Provided by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich