Carbon capture takes sponge-like form with new cost-effective method
An international team of scientists is using porous, sponge-like materials that can trap carbon dioxide in their cavities while allowing other gases such as nitrogen to pass through.
The materials are made from sugar and low-cost alkali metal salts, so they would be inexpensive enough for large-scale deployment, and they could be particularly effective for limiting the environmental damage of coal-fired power plants.
The team's paper is published in Angewandte Chemie, a publication of the German Chemical Society. Phillip Milner, assistant professor of chemical and chemical biology at Cornell University, led the collaboration.
For the last 100 years, the leading method for carbon capture in chemistry has been a process known as amine scrubbing. Amines are organic, ammonia-derived compounds that contain nitrogen. In an aqueous solution, they are able to selectively remove carbon dioxide from gas mixtures. However, oxygen degrades them every time they're cycled, which means that more and more of the material would need to be produced, thus driving up the cost.
Rather than trying to figure out how to overcome the oxidation problem in amines, Milner's lab has been experimenting with a different family of materials and designing them specifically for carbon dioxide capture.
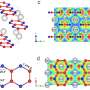
The new project focuses on sponge-like materials containing hydroxide sites in their pores. Typically, solutions of hydroxide salts reversibly react with carbon dioxide and form bicarbonate salts, such as baking soda, trapping the carbon dioxide. But in order to regenerate the hydroxide salt, the material needs to be heated up to 500 to 800 degrees Celsius—no easy feat, and not a cheap one, either.
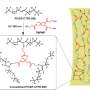
Lead author and doctoral student Mary Zick found that by incorporating bundles of sugar molecules called cyclodextrins as a starter and boiling them with alkali metal salts in water, she could create a sponge-like material that is riddled with cavities in which carbon dioxide binds strongly, but in which other gases such as nitrogen pass easily through.
"Coal emissions are still the No. 1 anthropogenic contributor to carbon-dioxide emissions in the world," Milner said. "What's nice about this work is that Mary not only found a material that's useful for carbon-dioxide capture from coal flue gas, but she outlined the structure-property relationships that will allow us to design materials for other applications, like capturing CO2 from natural gas-fired power plants, as well as maybe even from air, which is one of the really big challenges of our time."
More information: Mary E. Zick et al, Carbon Dioxide Capture at Nucleophilic Hydroxide Sites in Oxidation‐Resistant Cyclodextrin‐Based Metal‐Organic Frameworks, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2022). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202206718
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition , Angewandte Chemie
Provided by Cornell University