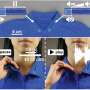
Specially designed slicker captures horse's vital signs on a laptop via Bluetooth
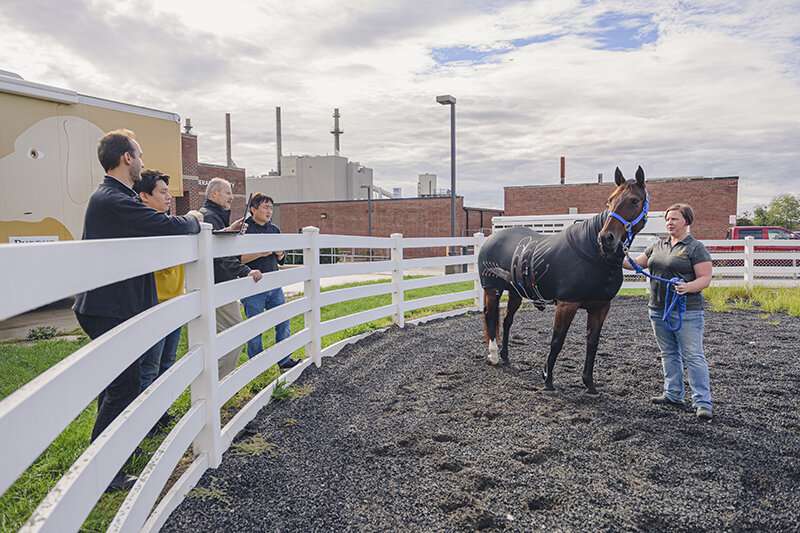

With the exception of Mister Ed of television sitcom fame, horses can't talk with humans about health issues.
Now, a first-of-its-kind horse slicker with a specially designed liner could be able to "tell" the horse's human caregivers of increasing chronic diseases.
A new study by Purdue University engineers and veterinarians explores how to convert off-the-shelf horse slickers into e-textiles that continuously monitor equine cardiac, respiratory and muscular systems for several hours under ambulatory conditions.
The study is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
To add the e-textile capabilities to the slicker, the Purdue team developed a dual regime spray and technique to directly embed a pre-programmed pattern of functional nanomaterials into the slicker's fabrics. To enable remote monitoring, the e-textile was connected to a separate portable unit that shared vital signs to a laptop via Bluetooth.
Using the e-textile means that veterinarians and their support staff won't have to shave the horse's hair or use messy adhesives to place the electrode on the horse's skin, which makes it more comfortable for the horse.
Chi Hwan Lee, the Leslie A. Geddes associate professor in Purdue's Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, said continual monitoring through the e-textile patterns can be useful for long-term management of chronic health conditions in large animals and eventually humans. Lee also has a joint appointment in the School of Mechanical Engineering and a courtesy appointment in the School of Materials Engineering.
According to Lee, adding e-textile properties to existing garments helps scientists, researchers and clinicians take advantage of garments' already-existing ergonomic designs to secure a commercial grade of wearability, comfortability, air permeability and machine washability.
"These specially designed e-textiles can comfortably fit to the body of humans or large animals under ambulatory conditions to collect bio-signals from the skin such as heart activity from the chest, muscle activity from the limbs, respiration rate from the abdomen or other vital signs in an extremely slight manner," Lee said. "Our technology will significantly extend the utility of e-textiles into many applications in clinical settings."
The team's next steps involve developing continuous 24-hour monitoring of horses with chronic disease or those receiving care in a veterinary ICU.
"We believe that our technology will be helpful in diagnosis or management of chronic diseases," Lee said, especially as demand increases for remote health monitoring.
"Remote health monitoring under ambulatory conditions would be useful for farm and household animals, as it could potentially minimize clinic visits, especially in rural areas. It would also increase the efficiency in managing a large number of farm/household animals at once from a distance, even overnight," Lee said.
A real-life example would be the ability to monitor severe equine asthma, which affects 14% of adult horses.
"Continuous monitoring would allow early detection of disease flair-up before it gets serious, offering an opportunity to nip it in the bud," said Laurent Couëtil, a professor of large animal internal medicine in Purdue's College of Veterinary Medicine and collaborator in the study. "Remote monitoring opens the possibility of sending vital information to the veterinarian to help make timely and informed treatment decisions."
More information: Taehoo Chang et al, A Programmable Dual‐Regime Spray for Large‐Scale and Custom‐Designed Electronic Textiles, Advanced Materials (2021). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202108021
Journal information: Advanced Materials
Provided by Purdue University