Regenerative medicine: Spider silk Janus fibers could attract nerve cells and stimulate their growth
Spider silk has enormous potential in regenerative medicine thanks to being a natural fiber that is tough, stable, and biodegradable. Researchers have now produced double-sided spider silk fibers, which could provide damaged nerve or muscle cells with a platform for growth. As the researchers report in the journal Angewandte Chemie, one side of the fibers is suitable for cell adhesion, while the other side could be used to attach factors or other substances.
Spider silk is nontoxic, biocompatible, and attracts virtually no microbes. These properties make it an ideal candidate as a supporting medium for nerve cells to grow along. However, in spider silk's original form, this process can take a very long time and requires complicated preparative steps. With this in mind, materials scientist Thomas Scheibel from the University of Bayreuth, Germany, along with his team, optimized the natural product in more than one way simultaneously, using a biotechnological approach.
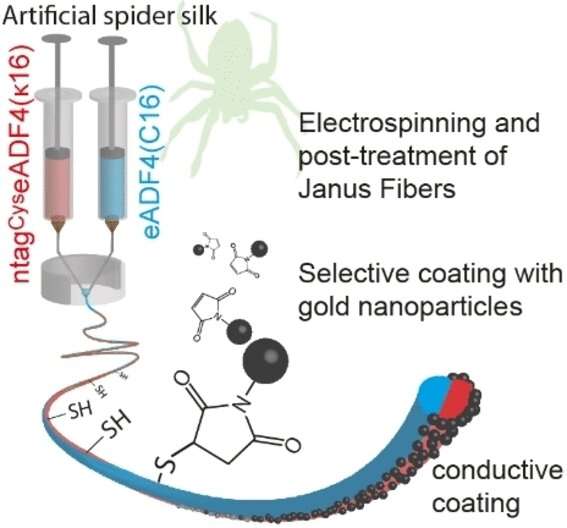
Scheibel's team produced spider silk using a genetically modified microorganism. "This gives us advantages in terms of quality," Scheibel explains, "and makes it possible to modify the proteins." The team not only modified one spider silk protein, but produced Janus spider silk fibers containing two differently optimized proteins in one material.
Janus fibers get their name from the famous Roman god thanks to their two "faces" or sides. One side of the fibers was formed from a spider silk protein in which the team substituted a single amino acid. This reversed the net charge (from negative to positive) of the protein: "the surface of the material then becomes more attractive to cells," explains Scheibel.
The other side of the fibers was formed from a spider silk protein to which the team added the amino acid cysteine. The addition of cysteine makes it possible to employ "click chemistry," a method for functionalizing materials in which the reaction partners react so easily with one another that it is as if they have been simply "clicked" together.
The team produced a two-sided, water-soluble fibrous material by using side-by-side electrospinning, which involves drawing out a thread from a protein solution in an electrical field. Post-treatment produced the Janus spider silk fibers as a crystalline, insoluble material. The fiber was then specifically coated on one side with gold nanoparticles using click chemistry, which made the spider silk electrically conductive, allowing the success of the modification to be directly measured.
Janus spider silk fibers coated with gold nanoparticles could be used to stimulate the growth of muscle cells. "Muscles are excited by electrical impulses, which could be produced using a 'gold wire' made of spider silk fibers," Scheibel explains. However, other modifications could be even more promising; the researchers are also investigating attachment of growth factors using click chemistry. These would not only promote cell adherence to the surface but also targeted and quicker growth of nerve cells along a splint.
More information: Gregor Lang et al, Site‐Specific Functionalization of Recombinant Spider Silk Janus Fibers, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2022). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202115232
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition , Angewandte Chemie
Provided by Wiley