New molecules could be used to treat autoimmune diseases in the future

When something is awry with your immune system, your digestion or your endocrine systems, nuclear receptors, as they are called, may well be involved. If need be, the operation of these regulator proteins can be altered with medicinal drugs, but this carries the very real risk of unpleasant side effects. Doctoral candidate Femke Meijer looked for—and found—molecules that might well be used as medications for autoimmune diseases, but with fewer side effects. Meijer defends her thesis at the department of Biomedical Engineering on June 23.
Our body has exactly 48 types of nuclear receptor. These are proteins that float about in our cells and can be activated by all sorts of signal molecules such as hormones. When this happens, the nuclear receptor in question issues an instruction in the cell nucleus to produce other particular proteins. Shutting down or conversely activating these nuclear receptors is the mechanism by which one in six medicines achieves its intended effect. The best-known example is most probably the contraceptive pill. "This acts on the estrogen and progesterone receptors," says doctoral candidate Femke Meijer.
As part of her research, Meijer studied another nuclear receptor, RORỿt, which regulates the production of cytokines and as such plays a role in the genesis of inflammatory reactions. Certain drugs for autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatism, psoriasis, asthma, and Crohn's disease, turn this function to their advantage and aim to shut down this nuclear receptor. "They do this by blocking what's known as its binding site with a molecule, so that this particular nuclear receptor, RORỿt, is deactivated," explains Meijer.
Side effects
Unfortunately, the binding sites of all 48 nuclear receptors are fairly similar. As a result, these drugs carry the risk of inadvertently affecting other nuclear receptors with very different functions.
As Meijer is keen to emphasize, this can lead to unwanted side effects. For example, weight gain in the case of prednisone—which combats inflammatory reactions—because this drug also affects our metabolism. And just think of the nuclear receptors on which the contraceptive pill acts; you wouldn't want a drug for rheumatism to leave you infertile.
In 2015, in the Chemical Biology group led by Professor Luc Brunsveld, which is where Meijer conducted her doctoral research, RORỿt was discovered to have a special property: as well as the usual binding site—the 'front door'- this nuclear receptor also possesses a 'back door' to which other molecules can bind. Marcel Scheepstra, then a doctoral candidate in the group, found a molecule that always blocked the effect of RORỿt, regardless of whether natural hormones were present. As a rule, in high concentrations, hormones reduce the effectiveness of drugs that work in this way.
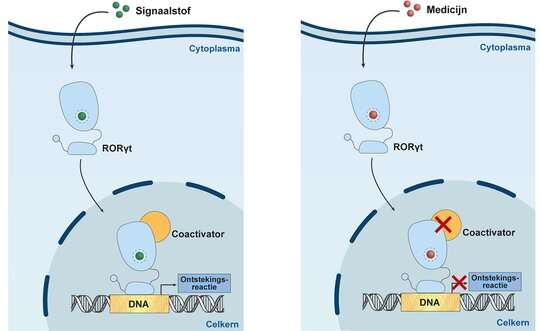
This is a very promising result, especially since this molecule proved to have no impact on almost all other nuclear receptors. The newly discovered molecule—which can be referred to as a 'key' - did not fit the regular binding site, whereas it did fit the back door, and this door, as far as anyone knows, is unique to RORỿt.
Femke Meijer's work builds on this result. First, it makes sense to have another key to the back door in reserve as a potential medicine. Secondly, the back-door key found by Scheepstra had two drawbacks, as she explains: "That molecule was quickly broken down in the body. What's more, it proved capable of binding to one other nuclear receptor, at its regular binding site."
Meijer then trawled through a computer database of some hundred thousand molecules in search of a 'key' with the right shape and chemical properties to fit the RORỿt's back door. "In the top 100 candidates that resulted from this search, we kept seeing a certain type of molecule crop up. In the lab, we produced a number of different versions of this molecule and introduced RORỿt to see whether they would bind to the molecules."
A number of steps later, involving repeated tweaking of the new versions, the binding was just about working, but it was still not very strong. "On a positive note, however, we were seeing the candidate molecules arrive at the right place in the protein. At this point, we replaced one nitrogen atom with an oxygen atom," says Meijer. This proved to be the right choice. "The optimized molecule binds much more securely to RORỿt and only to RORỿt; it binds less well to the 'wrong' nuclear receptor," adds Meijer.
Medicine
With this second key to the back door, Meijer believes she has found an interesting prospect for a new drug for autoimmune diseases, one that is expected to produce fewer side effects. What's more, a drug that uses the nuclear receptor's 'back door' could even prove to be more effective, because it doesn't have to compete with the body's hormones—which, after all, always enter by the 'front door."
But Meijer warns, a medicinal product is still a long way off. "While we have proven the molecule's effectiveness in cells, we have yet to prove the same with living organisms, such as animals or people. My colleagues are already working on this." As for herself, Meijer will be bidding the university farewell after her Ph.D. conferral ceremony and will start work at Symeres in Nijmegen, a company doing pharmaceutical research. "In my new role, I'm going to be able to do the same type of research as at TU/e, but then closer to the application. "For real' as it were. I'm excited by the prospect."
More information: 'Exploring Allosteric Modulation of the Nuclear Receptor RORỿt from a Drug Discovery Perspective'. Supervisors: Luc Brunsveld (TU/e) and R.G. Doveston (University of Leicester).
Journal information: ACS Chemical Biology
Provided by Eindhoven University of Technology