An economical alloy-based aerogel as electrocatalyst for carbon fixation
Many industrial processes emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, however, current electrochemical separation methods are expensive and consume large amounts of power. They also require expensive and rare metals as catalysts. A study in the journal Angewandte Chemie describes a new aerogel electrocatalyst formed from an inexpensive metal alloy, which enables highly efficient electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide. The main product is formic acid, which is a nontoxic basic chemical.
Capturing and chemically fixing carbon dioxide from industrial processes would be a huge step towards carbon neutrality. To prevent the notorious greenhouse gas from escaping into the air, it can be compressed and stored. Another option is electrochemical conversion to give other carbon compounds.
However, due to high power consumption and the cost of catalysts, electrochemical separation methods cannot be used on an industrial scale. This prompted Tianyi Ma of Swinburne University of Technology in Hawthorn, Australia, and colleagues to investigate replacement materials. The electrocatalysts currently used are made from precious metals such as platinum and rhenium. They catalyze electrochemical carbon fixation processes very efficiently, but they are also very expensive.
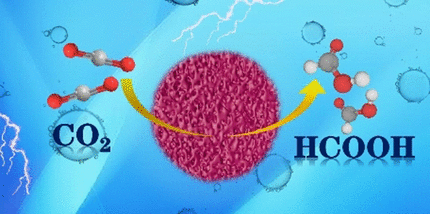
The authors discovered that the nonprecious metals tin and bismuth can form aerogels, which are incredibly light materials with particularly promising catalyst properties. Aerogels contain an ultraporous network that promotes electrolyte transport. They also offer up abundant sites where the electrochemical processes can take place.
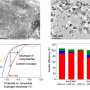
To produce the aerogels, the team mixed a solution of bismuth and tin salts with a reducing agent and a stabilizer. Simply stirring this mixture led to a stable hydrogel of a bismuth–tin alloy after six hours at room temperature. A straightforward freeze-drying process produced the aerogel, formed of loosely interwoven and branched nanowires.
The authors found the bimetallic aerogel performed outstandingly well for carbon dioxide conversion. Compared to pure bismuth, pure tin, or the non-freeze-dried alloy, a significantly higher current density was observed. The conversion took place with an efficiency of 93%, which was at least as efficient, if not more so, than the standard materials currently used, indicating a low-waste process.
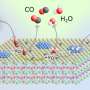
The process showed "excellent selectivity and stability for the production of formic acid under normal pressure at room temperature." The only byproducts were carbon monoxide and hydrogen formed in miniscule amounts. The authors explain that this selectivity and stability was a result of the energy conditions at the surface of the alloy. Here, the carbon dioxide molecules accumulate in such a way that the carbon atom is free to bind hydrogen atoms from water molecules. This gives formic acid as the favored product.
This research hints at positive future prospects for other combinations of metals. It is likely that other nonprecious metals would convert to aerogels, forming inexpensive, nontoxic, and highly efficient catalysts for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction.
More information: Zexing Wu et al. Engineering Bismuth–Tin Interface in Bimetallic Aerogel with a 3D Porous Structure for Highly Selective Electrocatalytic CO 2 Reduction to HCOOH, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2021). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202102832
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie , Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by Wiley