Electric cable bacteria breathe oxygen with unheard efficiency

Ten years ago, researchers at Aarhus University, Denmark, reported the discovery of centimeter-long cable bacteria, that live by conducting an electric current from one end to the other. Now the researchers document that a few cells operate with extremely high oxygen consumption while the rest of the cells process food and grow without oxygen. An outstanding way of life.
We humans need food and oxygen to live.
Now, imagine if oxygen was to be found only at the mountain top and food only in the valley. That's what the world looks like for cable bacteria, which live in the bottom of seas and lakes. For them, oxygen is available only at the very surface of the bottom, whereas the food is buried centimeters down.
Biowires
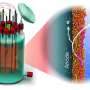
"While other organisms try to solve the problem by moving oxygen and food up and down, cable bacteria have developed electric wires. When consuming food they produce electrons and send them through the 'biowires' to the surface for reduction of oxygen from the overlying water," says Lars Peter Nielsen, head of Center for Electromicrobiology, Aarhus University, Denmark.
A cable bacterium consists of many cells in line. It can grow centimeters long, the cells encased in a common coat wherein the wires stretch.
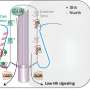
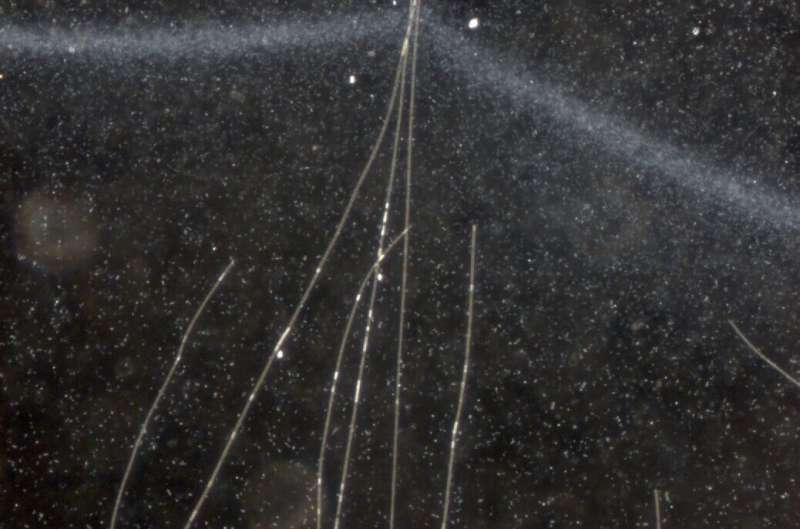
The researchers placed cable bacteria in a small, transparent chamber. In the middle, the bacteria had access to oxygen-free mud stuffed with food, while oxygen diffused in from the edges. Right where the intruding oxygen was depleted, numerous unicellular bacteria formed a distinct front. In that specific position they fought to capture food and oxygen from either side simultaneously.
"In the microscope, I watched how single cable bacteria placed themselves across the front with one end into the zone with oxygen," explains Stefano Scilipoti, Ph.D. student at Center for Electromicrobiology, Aarhus University and the primary discoverer.

Less than 10% of the cells are "breathing"
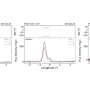
Scilipoti watched how one single cable bacterium could distort the front made by unicellular, swimming bacteria. The cable bacterium respired so much oxygen that the unicellular bacteria had to move closer to the edge of the chamber to sustain the oxygen supply needed for their respiration. The cable bacterium could just dip a few cells in oxygen, and the magnitude of the distortion—in laboratory jargon called 'bump'— allowed them to calculate how much oxygen was being consumed.
"Less than 10% of the cells of the cable bacterium consumed oxygen but they did it with a rate matching the highest rates known in biology. That only works because the cable bacterium runs an electric current between the cells being in contact with oxygen and the cells processing the food. The cells consuming oxygen can thus focus on this task only, while the other cells digest food and generate new cells," says Scilipoti.
The cable bacterial machinery
The ancestors of cable bacteria lived without any oxygen. Anaerobic bacteria, as you call them. For these bacteria, oxygen is toxic and a prolonged exposure eventually lead them to death. With the evolution of electric connection to oxygen however, cable bacteria can explore the strength of breathing with oxygen without exposing many cells to oxygen stress, thus getting the best of oxygen (more energy) and avoiding the rest (damage to the cells).
At Center for Electromicrobiology, the pursuit to unravel the special mechanisms that enable this unique electric form of life continues.
The study is published in Science Advances.
More information: "Oxygen consumption of individual cable bacteria" Science Advances (2021). advances.sciencemag.org/lookup … .1126/sciadv.abe1870
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by Aarhus University