New findings shed light on development of liposome-based inhibitors
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the biggest global public health challenges. However, the pathogenesis of AD is still unclear.
A number of studies showed that cell membranes play crucial roles in the progress of AD, particularly amyloid-β (Aβ) accumulation. Therefore it's essential to investigate the effect of biological membranes on amyloid formation.
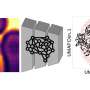
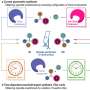
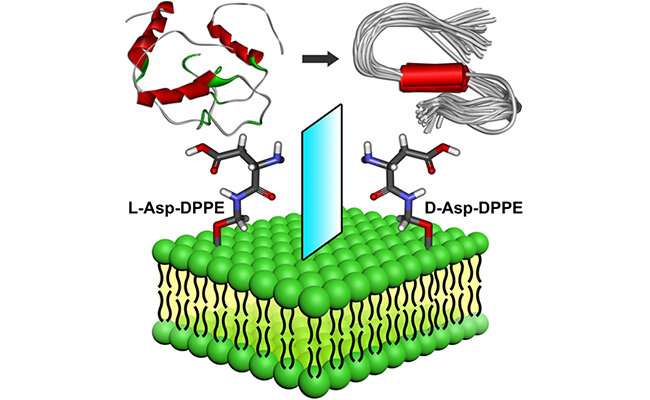
Recently, research groups led by Prof. Qing Guangyan and Prof. Li Guohui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences designed and prepared a pair of chiral amino acid-modified phospholipids, showing remarkable influence of molecular chirality of chiral liposomes on amyloid formation.
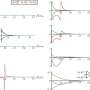
The researchers found that the self-assembled L-liposomes slightly inhibited Aβ(1-40) nucleation process but could not affect oligomer elongation process. By comparison, the D-liposomes strongly inhibited both the nucleation and elongation processes of Aβ(1-40).
Chiral liposomes not only had good biocompatibility but also could rescue Aβ(1-40) aggregation induced cytotoxicity with significant chiral discrimination, in which the cell viability was higher in the presence of D-liposomes.
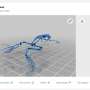
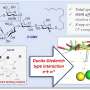
Meanwhile, the scientists revealed the binding site, binding manners and driving force between Aβ(1-40) and chiral phospholipid surfaces through detailed molecular dynamics simulations.
These findings expanded the research from artificial chiral surfaces to real chiral phospholipid surfaces, providing a deeper and real insight to understand the crucial amyloidosis process from the perspective of chiral biointerface.
Liposomes have convincing biocompatibility, and the convergence of liposomes with non-natural D-amino acids as amyloid inhibitors are promising in early prevention and treatment of AD, which points out a clear direction for the development of liposome-based inhibitors.
The study was published in Chemical Science on June 25.
More information: Xue Wang et al. Molecular chirality mediated amyloid formation on phospholipid surfaces, Chemical Science (2020). DOI: 10.1039/D0SC02212H
Journal information: Chemical Science
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences