Why does your cotton towel get stiff after natural drying?
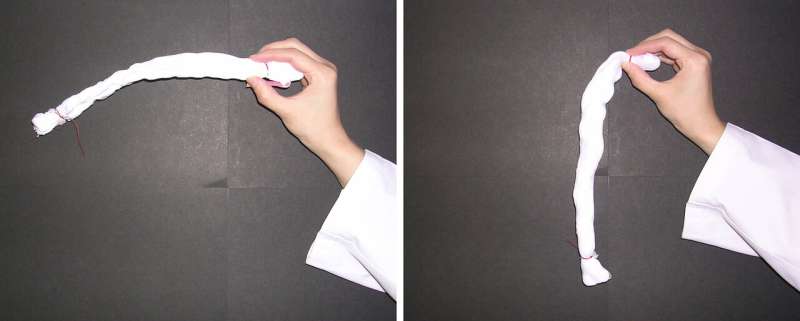
The remaining "bound water" on cotton surfaces cross-link single fibers of cotton, causing hardening after natural drying, according to a new study conducted by Kao Corporation and Hokkaido University. This provides new insight into unique water behaviors on material surfaces and help researchers develop better cleaning technologies.
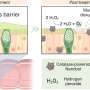
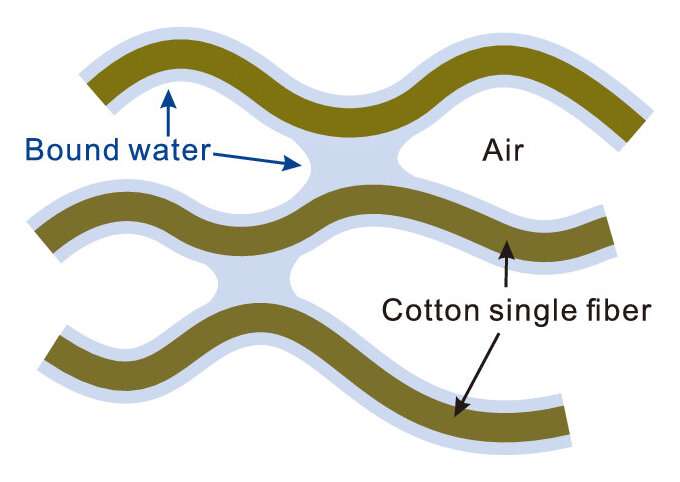
Cotton towels often become stiff when washed without fabric softener and naturally dried, but the mechanism behind it has remained a mystery. In previous studies, the research groups at Kao Corporation suggested the involvement of bound water—a special type of water that exhibits unique properties on the surface of materials—for the hardening. The group proposed a theoretical model in which the bound water that remains on the surface of cotton causes cross-linking between single fibers through a process called capillary adhesion.
In the current study published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry C, the research group reports direct observations of the bound water on cotton surfaces, providing strong evidence for Kao's model. Joined by Ken-ichiro Murata of Hokkaido University, the group employed special analytical techniques called atomic force microscopy (AFM) and AFM-based infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR) to investigate the bound water on cotton surfaces at the molecular level.
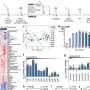
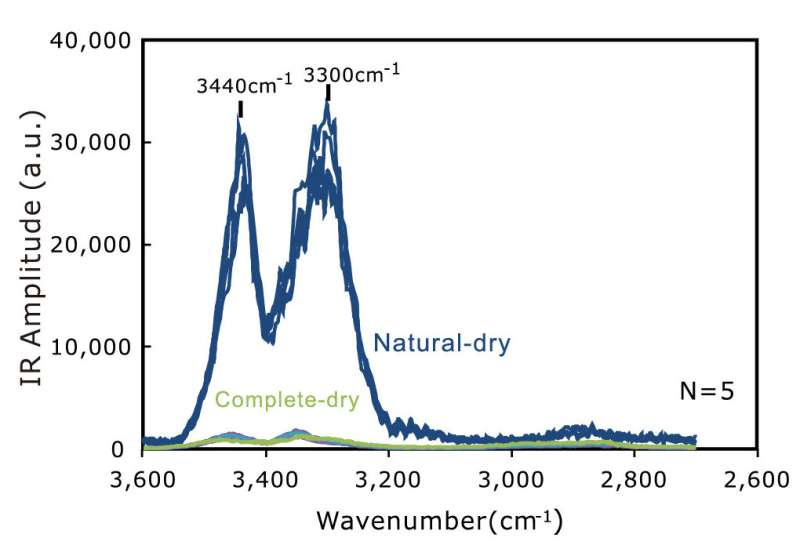
The AFM observations indicated the existence of a viscous substance on the cotton surface that is not cellulose, the major component of cotton. This strongly suggested viscous bound water is present and causing capillary adhesion—a phenomenon in which liquid sandwiched between solid surfaces causes them to adhere. In the following experiments, the AFM-IR spectra of naturally dried cotton surfaces showed two peaks that indicate the existence of water. On the other hand, no peaks were observed after completely removing water on the cotton surface. Furthermore, the spectra, showing two clear peaks, suggested that the bound water takes two different states at the air-water interface and the water-cotton interface, respectively.
"The experiments clarified that bound water is evident on cotton surfaces and contributes to certain dynamic properties such as stiffness mediated by capillary adhesion. Also, the bound water itself manifested a unique hydrogen bonding state different from that of ordinary water," said Ken-ichiro Murata of Hokkaido University. Takako Igarashi of Kao Corporation added, "It has been thought that fabric softeners reduce friction between cotton fibers. However, our results showing the involvement of bound water in the hardening of cotton provide new insight into how fabric softeners work and can help us develop better agents, formulations and systems."
More information: Takako Igarashi et al. Direct Observation of Bound Water on Cotton Surfaces by Atomic Force Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy–Infrared Spectroscopy, The Journal of Physical Chemistry C (2020). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c00423
Journal information: Journal of Physical Chemistry C
Provided by Hokkaido University