Superbug battle: Bacteria structure may be key to new antibiotics
Cornell researchers have uncovered the structure of a regulatory mechanism unique to bacteria, opening the door for designing new antibiotics targeted to pathogens.
As the threat of antibiotic-resistant germs grows, this discovery offers hope for finding an alternative way to target disease-causing bacteria.
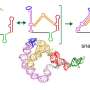
In the study, researchers used X-ray crystallography to reveal the structure of so-called "T-box" elements in the pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the model bacterium in the study.
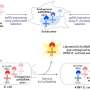
T-boxes are structures that recognize when a cell is deficient in a specific amino acid, the building blocks of cells. T-boxes allow bacteria to respond to this deficiency by initiating a process that generates more of that amino acid. In this way, T-boxes facilitate basic functioning in bacteria, including many pathogens such as M. tuberculosis and Bacillus anthracis, which causes the deadly anthrax disease.
"The T-boxes are only found in bacteria and they control essential genes," said study first author Robert Battaglia. "This makes them an attractive target because they are also essential for a lot of these bacteria to respond to starvation conditions."
Battaglia is a graduate student in the lab of senior author Ailong Ke, professor of molecular biology and genetics at Cornell University.
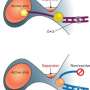
T-boxes bind to an essential macromolecule called tRNA, which exists in uncharged and charged forms. Different types of tRNA are each fitted to a specific type of amino acid. When the amount of an amino acid is low in the bacteria cell, the corresponding tRNA will be uncharged and will bind to a T-box, which in turn recognizes what type of amino acid that tRNA requires and facilitates a process of generating more of that amino acid. When the amount of an amino acid goes up, the tRNA will couple with it, thereby charging that tRNA. The amino acids are then used in all kinds of basic bacteria cell functions.
In the study, the researchers described the structure of the full T-box and tRNA complex.
"By solving our structure, we're able to see how different parts of the T-box are positioned to allow the T-box to have this specific interaction with a tRNA," Battaglia said. "If we can develop some sort of drug to target these T-box elements to mess with their ability to bind with the tRNA, they could be a really good choice for an antibiotic because we don't have [T-boxes] ourselves, so we don't have to worry about side effects or toxicity."
The study was published in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology.
More information: Robert A. Battaglia et al, Structural basis for tRNA decoding and aminoacylation sensing by T-box riboregulators, Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41594-019-0327-6
Journal information: Nature Structural & Molecular Biology , Nature Structural and Molecular Biology
Provided by Cornell University