Milestone for bERLinPro: Photocathodes with high quantum efficiency

Teams from the accelerator physics and the SRF groups at HZB are developing a superconducting linear accelerator featuring energy recovery (Energy Recovery Linac) as part of the bERLinPro project. It accelerates an intense electron beam that can be used for applications like generating brilliant synchrotron radiation. After use, the electron bunches are directed back to the superconducting linear accelerator, where they release almost all their remaining energy. This energy is then available for accelerating new electron bunches.
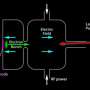
A crucial component of the design is the electron source. Electrons are generated by illuminating a photocathode with a green laser beam. The quantum efficiency, as it is called, indicates how many electrons the photocathode material emits when illuminated at a certain laser wavelength and power. Bialkali antimonides exhibit particularly high quantum efficiency in the region of visible light. However, thin films of these materials are highly reactive and therefore very sensitive, so they only work at ultra-high vacuum.
A HZB team headed by Martin Schmeißer, Dr. Julius Kühn, Dr. Sonal Mistry and Prof. Thorsten Kamps has now greatly improved the performance of the photocathode to make it ready for use with bERLinPro. They modified the manufacturing process for the photocathodes of cesium- potassium-antimonide on a molybdenum substrate. The new process delivers the desired high quantum efficiency and stability. Studies showed that the photocathodes do not degrade, even at low temperatures. This is a critical prerequisite for operation within a superconducting electron source, where the cathode must be operated at temperatures far below zero.
The physicists were able to demonstrate this performance with detailed studies: Even after its transport via the photocathode transfer system and introduction into the photo injector of the SRF, the quantum efficiency of the photocathode was still about five times higher than necessary to achieve the maximum electron-beam current needed for bERLinPro.
"An important milestone for bERLinPro has been reached. We now have the photocathodes available to generate the first electron beam from our SRF photoinjector at bERLinPro in 2019," says Prof. Andreas Jankowiak, head of the HZB Institute for Accelerator Physics.
More information: Martin A. H. Schmeißer et al, Towards the operation of Cs-K-Sb photocathodes in superconducting rf photoinjectors, Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (2018). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.21.113401
Provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres