Locating the production site of glucan in grass cell walls
Where an item is manufactured tells you a lot about it. Is it made by an assembly line or handcrafted one at a time? To learn more about glucose, the sugary feedstock of biofuel refineries, scientists want to know where a polymer of glucose, mixed-linkage glucan (MLG), resides in grasses as grass species are a major potential renewable biomass feedstock. Scientists from the center demonstrated that MLG is present primarily in the Golgi apparatus (flattened, stacked pouches near the cell's nucleus). These findings offer new insight and new targets to maximize MLG production.
Increasing the content of easily digestible, six-carbon sugars can increase the fuel yield from bioenergy crops. This study adds to the understanding of the synthesis of glucose polymers, including where it is synthesized in cells and where it accumulates in plants. These findings could help guide engineered increases of MLG levels in plants.
Mixed-linkage glucan (MLG), a (1,3;1,4)-β-linked glucose polymer, is important for the structural integrity of the plant and a source of glucose that can be converted to biofuels and bioproducts within a biorefinery. MLG is present predominantly in the cell wall of grasses. It is synthesized by cellulose synthase-like enzymes, with CSLF6 being the best-characterized MLG synthase. Although the function of this enzyme in MLG production has been established, the site of MLG synthesis in the cell is debated. In this study, Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center researchers tested the various possibilities to establish a better understanding of the fundamentally important mechanisms of plant cell wall biosynthesis.
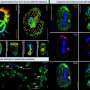
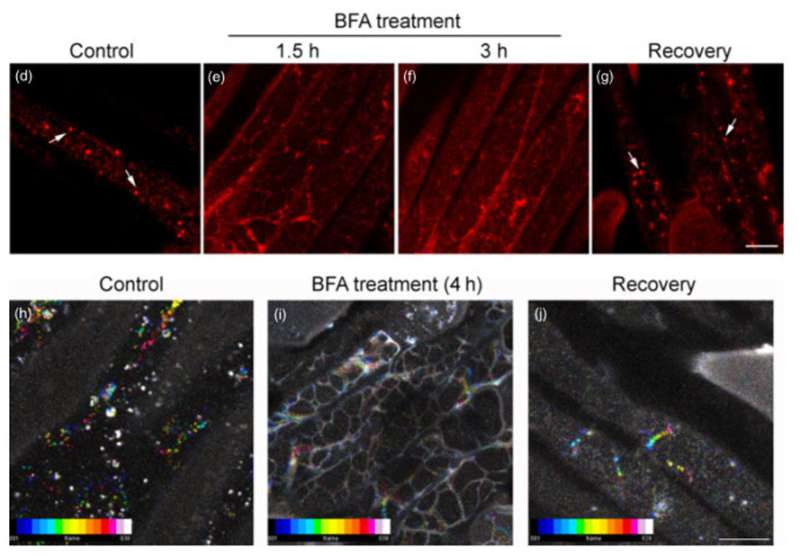
Using immuno-localization analyses with MLG-specific antibody in Brachypodium and in barley, MLG was identified in the Golgi, in post-Golgi structures, and in the cell wall. Analyses of a functional fluorescent protein fusion of CSLF6 stably expressed in Brachypodium demonstrated that the enzyme is localized in the Golgi. Further, the team demonstrated that the overproduction of MLG caused developmental and growth defects in Brachypodium and barley. Together, these results indicate that MLG production occurs in the Golgi similar to other cell wall matrix polysaccharides and supports the broadly applicable model that MLG accumulation is under tight control in the cell wall during development and growth. Future studies that build on this work will enable scientists to develop strategies that increase MLG levels in bioenergy crops.
More information: Sang-Jin Kim et al. In the grass species Brachypodium distachyon , the production of mixed-linkage (1,3;1,4)-β-glucan (MLG) occurs in the Golgi apparatus, The Plant Journal (2018). DOI: 10.1111/tpj.13830
Journal information: The Plant Journal
Provided by US Department of Energy