Researchers break data transfer efficiency record
Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have set a new record in the transfer of information via superdense coding, a process by which the properties of particles like photons, protons and electrons are used to store as much information as possible.
The ORNL team transferred 1.67 bits per qubit, or quantum bit, over a fiber optic cable, edging out the previous record of 1.63 per qubit.
The work by ORNL's Brian Williams, Ronald Sadlier and Travis Humble is published as "Superdense coding over optical fiber links with complete Bell-state measurements" in Physical Review Letters. The research was selected as an "Editor's Suggestion".
Whereas computers transmit information in the form of bits (generally represented by either a 1 or a 0), qubits can employ two states simultaneously and therefore represent more information than a traditional bit. The physics of this quantum communication task employed by Williams and his team is similar to that used by quantum computers, which use qubits to arrive at solutions to extremely complex problems faster than their bit-laden counterparts.
Williams' team was the first to use superdense coding over optical fiber, a major achievement in the quest to adopt quantum communication to modern networking technology. And because the team used conventional laboratory equipment such as common fiber optic cable and standard photon detectors, they have brought the technique one step closer to practical use.
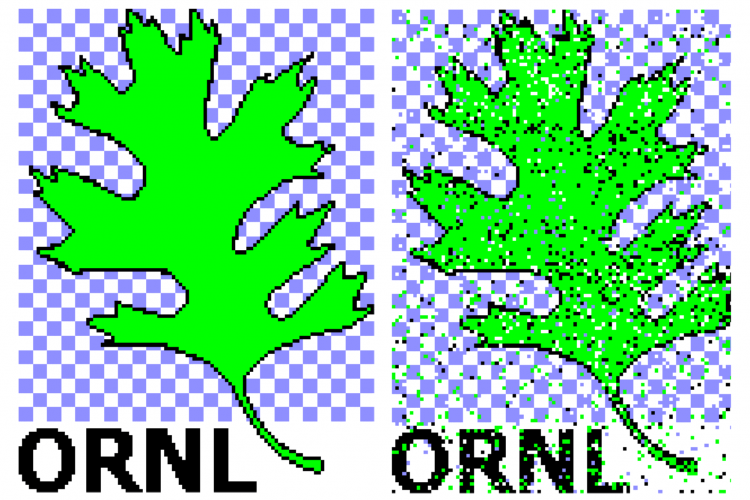
As a demonstration of the technique's effectiveness, the team transmitted the ORNL logo, an oak leaf, between two end points in the laboratory.
While the technology is at present largely experimental, practical applications could include a cost-effective way to condense and transfer information. This includes more efficient methods for transmitting and receiving data in application areas such as the Internet and cybersecurity.
"This experiment demonstrates how quantum communication techniques can be integrated with conventional networking technology," Williams said. "It's part of the groundwork needed to build future quantum networks that can be used for computing and sensing applications."
More information: Superdense Coding over Optical Fiber Links with Complete Bell-State Measurements, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 050501 – Published 1 February 2017. journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/ … ysRevLett.118.050501
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by Oak Ridge National Laboratory