Reduce energy consumption by 30 percent through ICT

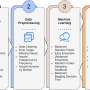
According to a European research project, cities may be able to reduce their energy consumption by 30 % by leveraging information and communication technologies (ICTs). This breakthrough was made by the ENERSIP project, which is formed by 10 partners from 5 European countries, and has received EUR 3.99 million in funding from the EU's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) under the theme for ICT support to energy-positive buildings and neighbourhoods. Their results were presented after analysis showed how to optimise the use of residential consumption and generation infrastructures.
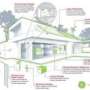
The scientists and researchers participating in the ENERSIP project, led by the Spanish company Tecnalia, have designed, developed, and validated an ICT platform that allows residential electrical consumption to be reduced by 30 %, while also integrating micro-generating installations using renewable energy, such as photovoltaic solar panels installed on the roofs of homes.
The key to this achievement is a result of a two-pronged strategy, firstly reducing the electricity consumption in homes (around 15 % to 20 %), and secondly adjusting the consumption and generation of electricity in districts (by the same amount). According to Professor José Ignacio Moreno, of Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) Department of Telematic Engineering, the system 'gives the users information regarding their consumption, allowing them to identify the appliances that use the most energy; it then suggests possible solutions, attempting to modify certain behaviours and fomenting good practices that allow consumers to reduce their electricity bill'. Through these means, the ENERSIP platform allows appliances to be monitored by networks of sensors and actuators so that they can be controlled wirelessly using web applications.
The ENERSIP project designed the system so that it carries out automatic actions allowing the consumption in homes within a district to be adjusted as much as possible so that they use renewable energy generated by sources from within the same district, reducing energy flows, and as a consequence, energy losses and costs. 'This type of action falls within what is known as electricity demand management,' said Gregorio López, another of the UC3M researchers.
For example, he added, the temperature could be raised by a few degrees in the summer (or lowered in winter) in hundreds of thousands of homes during the periods of lowest production of renewable energy in a district, or the programmed running of certain appliances (dishwashers, washing machines) can be moved to a time period when renewable energy production is at its peak. 'Of course,' López pointed out, 'those households would have agreed in advance to participate in this type of program in exchange for certain incentives, and pre-established levels of comfort would never be compromised.'
One of the benefits of the ENERSIP platform is that it only needs a few basic ICT installations to make it work. Specifically, it would require networks with sensors and actuators for the consumption and micro-generation infrastructures, an Internet connection and a web application that would allow access from any device connected to the Web (although the ENERSIP project itself also uses a dedicated core communications infrastructure that offers certain advantages). 'It could be implemented from any home equipped with the typical consumer infrastructure or consumer and micro-generation infrastructure,' José Ignacio Moreno explained.
The team he heads at UC3M was in charge of the formal design and modelling of the communications architecture of the ENERSIP platform, as well as the software simulations to evaluate the performance of that architecture. He participated in the design and definition of the platform's integration and validation phases and presented research progress through technical articles at key communication conferences, such as INFOCOM 2011 and ICC 2012.
More information: www.enersip-project.eu/
Provided by CORDIS