Rewinding development: A step forward for stem cell research
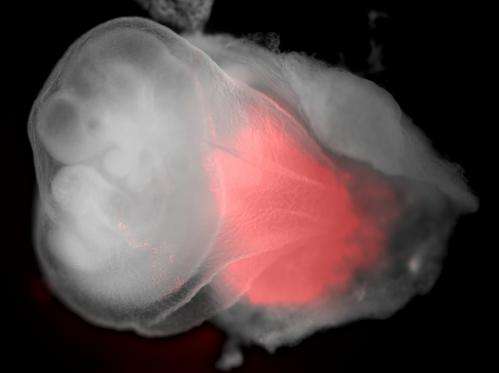
Scientists at the Danish Stem Cell Center, DanStem, at the University of Copenhagen have discovered that they can make embryonic stem cells regress to a stage of development where they are able to make placenta cells as well as the other fetal cells. This significant discovery, published in the journal Cell Reports today, has the potential to shed new light on placenta related disorders that can lead to problematic pregnancies and miscarriages.
Embryonic stem cells can make all kinds of adult cells in the human body such as muscle, blood or brain cells. However, these embryonic stem cells are created at a point when the embryo has already lost the ability to make extra-embryonic tissue such as placenta and yolk sac. Extra-embryonic tissues are formed at the very earliest stage of development right after fertilization and are essential for the growth of the embryo and its implantation in the womb.
A team of scientists at the Danish Stem Cell Center, DanStem, at the University of Copenhagen have shown that it is possible to rewind the developmental state of embryonic stem cells. By maintaining mouse embryonic stem cells under certain conditions, they found that cells appear to regress and resemble extremely early embryo cells that can form any kind of cell including placenta and yolk sac cells.
"It was a very exciting moment when we tested the theory," says Professor Josh Brickman from DanStem. "We found that not only can we make adult cells but also placenta, in fact we got precursors of placenta, yolk sac as well as embryo from just one cell."
Sophie Morgani, PhD student at DanStem and first author of the paper, which was published in the scientific journal Cell Reports today adds: "This new discovery is crucial for the basic understanding of the nature of embryonic stem cells and could provide a way to model the development of the organism as a whole, rather than just the embryonic portion. In this way we may gain greater insight into conditions where extra-embryonic development is impaired, as in the case of miscarriages."
LIF protein plays a crucial role
Brickman and colleagues grew their embryonic stem cells in a solution containing LIF, which is a protein known to somehow support embryonic stem cells but also for its role in implantation of the embryo into the uterus. As implantation is stimulated by the cells that will become the placenta, not the embryo, these roles appeared to be contradictory. The DanStem study resolved this contradiction by revealing that LIF helps maintain the cells in their regressed, early stage of development.
"In our study we have been able to see the full picture unifying LIF's functions: What LIF really does, is to support the very early embryo state, where the cells can make both embryonic cells and placenta. This fits with LIFs' role in supporting implantation," Josh Brickman says.
Journal information: Cell Reports
Provided by University of Copenhagen















