This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Scientists study effect of boron nitride microribbon on ceramic properties
In recent years, the high complexity of integrated devices has made heat accumulation increasingly critical and has resulted in higher heat dissipation requirements for substrates and packaging materials. In this study, boron nitride microribbon (BNMR)/Al2O3 composite ceramics are prepared using spark plasma sintering (SPS).
This study examines the effect of varying the amount of toughened phase BNMR on the density, mechanical properties, dielectric constant, and thermal conductivity of BNMR/Al2O3 composite ceramics while also exploring the mechanisms behind the toughening and increased thermal conductivity of the fabricated ceramics.
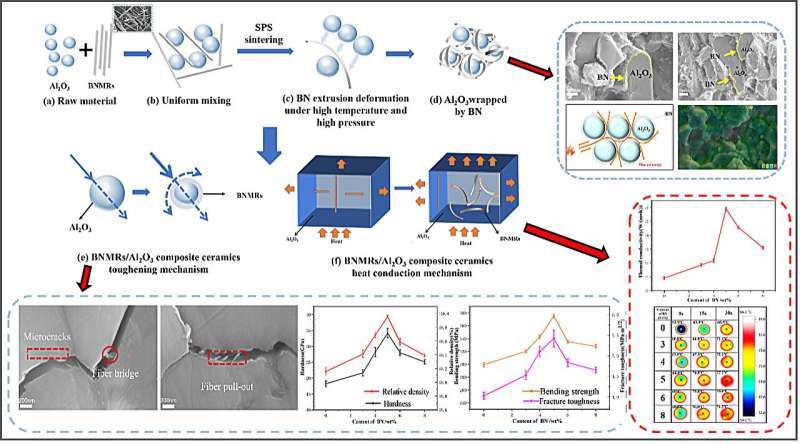
A team of material scientists led by Ji-Lin Wang from Guilin University of Technology in Guilin, boron nitride microribbon (BNMR)/Al2O3 composite ceramics are prepared using spark plasma sintering (SPS). During the sintering process, the pliable BNMRs were continuously extruded and deformed by the Al2O3 grains under high temperature and pressure, followed by even wrapping of the Al2O3 grains.
The BNMRs distributed between the Al2O3 grain boundaries reduced the atomic diffusion coefficient and inhibited the potential abnormal growth of Al2O3 grains. In this process, not only a special nuclear shell structure is formed, but also a good BN thermal conduction pathway is constructed, which better promotes the rapid conduction of heat.
The team published their review in the Journal of Advanced Ceramics on April 30, 2024.
"In this work, we prepared BNMR/Al2O3 composite ceramics, and during the sintering process, the pliable BNMRs were continuously extruded and deformed by the Al2O3 grains under high temperature and pressure, and as a result, not only did we form a special thermal conductivity pathway to enhance the thermal conductivity of the composites, but we also improved the mechanical properties of the Al2O3 ceramics," said Ji-Lin Wang, first author of this new paper, associate researcher of the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Guilin University of Technology.
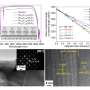
The BNMRs/Al2O3 composite ceramics composed of 3-4 um Al2O3 and 1-2 um BNMRs powders showed good overall performance, and for 5 wt% content of BNMRs composite ceramics, the relative densities, hardness, fracture toughness, and flexural strengths, respectively, were 99.95%±0.025%, 34.11±1.5 Gpa, 5.42±0.21 MPa·m1/2, and 375±2.5 MPa, and the thermal conductivity and dielectric constant were 6.18±0.02 and 15.89±0.13 W/(m·K), respectively. The fracture toughness, bending strength and thermal conductivity increased by 35%, 25% and 45.6%, respectively, compared with the corresponding values for pure Al2O3 ceramics.
The results of this study are promising to provide new experimental and theoretical references for improving the overall performance of high thermal conductivity alumina-based ceramic substrates.
The next work plan is to further improve the comprehensive performance of alumina Al2O3 based composite ceramic packaging substrates by introducing multiphase particles, whiskers or fibers to meet the needs of the latest electronic information technology development.
Additional study contributors include Dongping Lu, Weiping Xuan, Yuchun Ji, Shaofei Li, Wenbiao Li, Shilin Tang, Guoyuan Zheng and the corresponding authors Prof. Fei Long from Guilin University of Technology in Guilin, China; and Ruiqi Chen from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
More information: Jilin Wang et al, Boron nitride microribbons strengthened and toughened alumina composite ceramics with excellent mechanical, dielectric, and thermal conductivity properties, Journal of Advanced Ceramics (2024). DOI: 10.26599/JAC.2024.9220872
Provided by Tsinghua University Press