This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Scientists use magnetic nanotech to safely rewarm frozen tissues for transplant
Every day, people die waiting for an organ transplant. Time is at a premium, not just for those awaiting organs, but also for the organs themselves, which can deteriorate rapidly during transportation.
Looking to extend the viability of human tissues, researchers report inNano Letters their efforts to facilitate completely freezing, rather than cooling and then thawing, potentially life-saving organs. They demonstrate a magnetic nanoparticle's successful rewarming of animal tissues.
As of August 2024, more than 114,000 people are on the U.S. national transplant waiting list, according to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, and about 6,000 annually will die before receiving an organ transplant. One reason is the loss of organs in cold storage during transportation when delays cause them to warm prematurely.
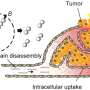
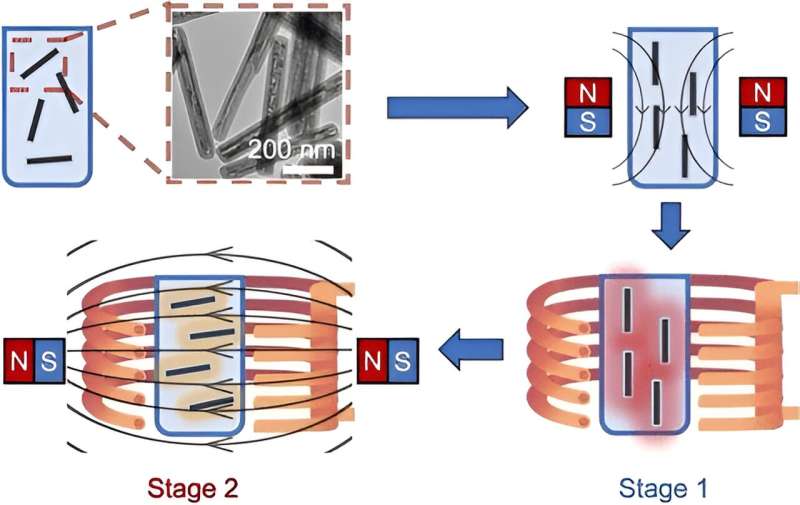
Methods have been developed to quickly freeze organs for longer-term storage without risking damage from ice crystal formation, but ice crystals can also form during warming. To address this problem, Yadong Yin and colleagues advanced a technique known as nanowarming, pioneered by collaborator John Bischof, to employ magnetic nanoparticles and magnetic fields to thaw frozen tissues rapidly, evenly and safely.
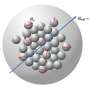
Recently, Yin and a team developed magnetic nanoparticles—effectively extremely tiny bar magnets—that, when exposed to alternating magnetic fields, generated heat. And that heat rapidly thawed animal tissues stored at -238 degrees Fahrenheit (-150 degrees Celsius) in a solution of the nanoparticles and a cryoprotective agent.
The researchers worried, however, that uneven distribution of the nanoparticles within the tissues might trigger overheating where the particles congregated, which could lead to tissue damage and toxicity from the cryoprotective agent at elevated temperatures.
To reduce these risks, the researchers have continued their investigation, working on a two-stage approach that more finely controls nanowarming rates. They describe this process:
- Cultured cells or animal tissues were immersed in a solution containing magnetic nanoparticles and a cryoprotective substance and then frozen with liquid nitrogen.
- In the first stage of thawing, as before, an alternating magnetic field initiated rapid rewarming of animal tissues.
- As the samples approached the melting temperature of the cryoprotective agent, the researchers applied a horizontal static magnetic field.
- The second field realigned the nanoparticles, effectively tapping the brakes on heat production.
The heating slowed fastest in areas with more nanoparticles, which dampened concerns about problematic hotspots. Applying the method to cultured human skin fibroblasts and to pig carotid arteries, the researchers noted that cell viability remained high after rewarming over a few minutes, suggesting the thawing was both rapid and safe.
The ability to finely control tissue rewarming moves us one step closer to long-term organ cryopreservation and the hope of more life-saving transplants for patients, the researchers say.
More information: Sangmo Liu et al, Magnetic-Nanorod-Mediated Nanowarming with Uniform and Rate-Regulated Heating, Nano Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c03081
Journal information: Nano Letters
Provided by American Chemical Society