This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
proofread
Australia's nature is in deep crisis. These three easy steps could give new environmental laws teeth

The Albanese government's environmental reforms are likely to feature prominently on federal parliament's agenda this week. A Senate inquiry into the long-awaited reforms is due to deliver its findings on Monday. Meanwhile, the Coalition is reportedly preparing to oppose the changes, potentially forcing Labor into negotiations with the Greens.
The so-called "nature positive" bills would establish two new agencies, Environment Protection Australia (EPA), an environmental regulator and watchdog, and Environment Information Australia (EIA), an environmental bureau of statistics.
Establishing the new agencies would deliver an election promise, but falls far short of the comprehensive and desperately needed package of reforms outlined in the Albanese government's Nature Positive Plan, launched in 2022.
While it may be too late for the full Nature Positive Plan this term, it's not too late to improve the current reform bills in Parliament and start achieving genuine improvements for nature. We propose three key amendments that could achieve that.
The background: biodiversity in crisis
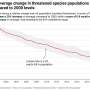
Australia's environmental laws need urgent overhaul. The 2021 State of the Environment report, like its predecessors, showed our catchments, waterways and native species are in serious and worsening decline.
This matters to all of us, as we depend on healthy ecosystems for the air we breathe, the water we drink, the food we eat and even our physical and mental health. Around half of our economy, such as the multibillion-dollar agricultural and tourism sectors, depends on the state of our environment.
Australia's main biodiversity legislation, the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act, hasn't had a major overhaul since it was enacted 25 years ago. In his 2020 review, Graeme Samuel found the laws to be ineffective, outdated and in need of fundamental reform.
The government responded to the Samuel Review by releasing the Nature Positive Plan. At the time, Environment Minster Tanya Plibersek said, "Native species extinction, habitat loss and cultural heritage destruction are all accelerating, and reform is urgently needed."
We couldn't agree more. That's why we propose these three changes to ensure the reforms actually start to benefit nature.
1: Bolster the new agencies
The new EPA and information agency could make a real difference for nature, if we get them right.
The government says the EPA should be a "tough cop on the beat". But its proposed governance structure is problematic.
The draft laws vest all the agency's power in a single person—a chief executive appointed by the minister. This leaves the chief executive vulnerable to pressures from all sides and to perceptions of ministerial influence.
Independence promotes trust. That's why we have joined many others in arguing the EPA should have an independent board. This would align the federal EPA with counterparts in the states and New Zealand.
Environment Information Australia should also have an independent board. The Australian Institute of Health and Welfare has one. This helps the states trust the institute with their health data by creating a buffer from direct Commonwealth control.
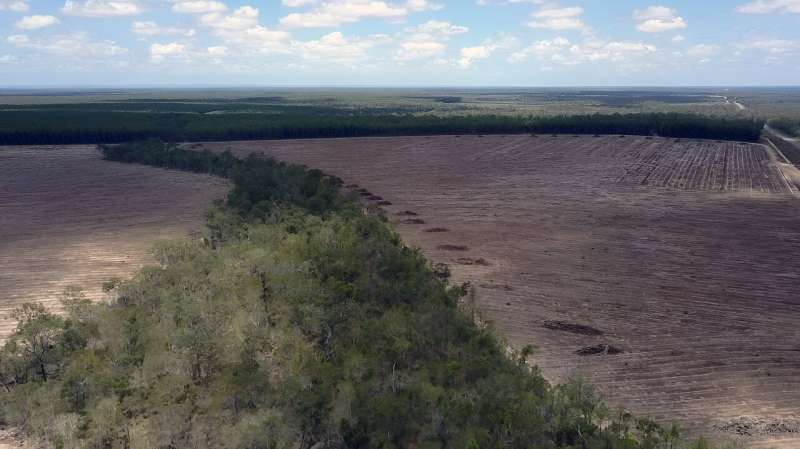

2: Set national environmental standards
Establishing national environmental standards was the centerpiece of both the Samuel Review and Labor's Nature Positive Plan.
These standards would set the bar for regulatory decisions, for example, by preventing development in areas of highest biodiversity value. They would also set goals and priorities for environmental plans and restoration programs.
In short, introducing standards could prevent decisions that degrade the environment, prioritize development in areas of lower conservation concern, and focus investment for recovery where it's needed the most.
Unfortunately, the federal government indefinitely deferred the standards—along with most of its other environmental reforms—after pressure from the state Labor government in Western Australia and the mining and resources industries.
The draft laws should be changed to at least grant the relevant minister the power to set environmental standards. This would enable the government to release initial standards in the next few months—so improvements for nature can start to be delivered.
3: Set a proper baseline from which to measure progress
The reforms center around the concept of "nature positive." The internationally agreed definition of the term is reversing the decline of species and ecosystems by 2030, measured against a 2020 baseline, and achieving recovery by 2050.
The bills, however, are vague, defining nature-positive as an improvement from an undefined "baseline" set by the information agency. This would allow a "trajectory of decline" to be chosen as the baseline.
For example, imagine a region with a population of 500 bilbies, which is declining by 50 bilbies a year due to feral predators. If that trajectory of decline was used as the baseline, then slowing bilby loss to 40 bilbies a year would qualify as nature-positive, even though, eventually, the region would have no bilbies.
We are calling for the baseline to be set at a recent year—such as 2020, the international standard. This is the type of baseline set under Australia's climate change laws, which aim to reduce Australia's greenhouse gas emissions to 43% below 2005 levels by 2030.
It might sound like technical detail, but it could be crucial. In the case of our bilbies example, it would mean that there should be at least 501 bilbies at a specified time in the future.
We also recommend the baseline year be enshrined in law to provide a permanent benchmark for measuring environmental change.
A way forward
A federal election is looming, and nature-positive laws are the Albanese government's headline environmental reform.
Four years after Samuel called for urgent reform, and two years after Plibersek promised it, laying weak foundations for reform is not good enough.
The changes we propose are important and feasible. The longer we delay, the harder it will be to achieve a "nature positive" future.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()