This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study investigates extreme precipitation events across diverse regions of the Tibetan Plateau
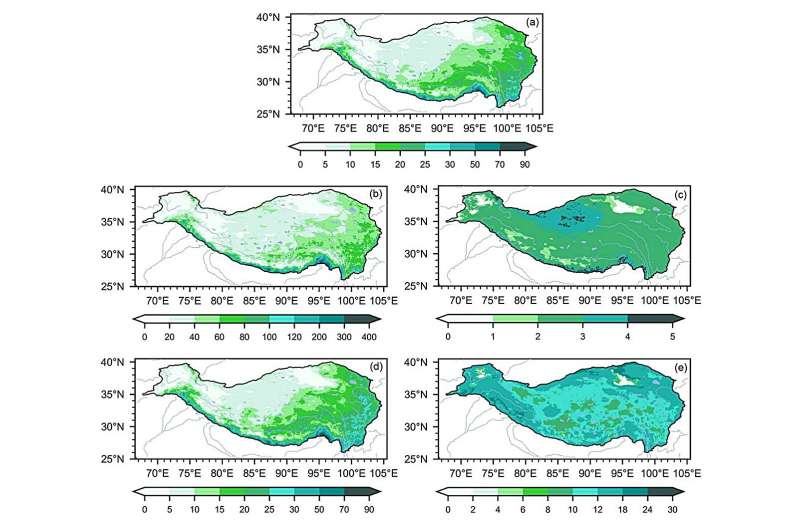
Researchers have identified three distinct spatial types for summer extreme precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau: Northwest, Southeast, and Southern Himalayas types based on predefined thresholds for extreme precipitation. The study is published in the journal Science China Earth Sciences.
The Northwest and Southeast types are primarily influenced by anomalous signals in the mid-to-high latitude regions upstream of them, while their wave train shapes exhibit significant differences. The precursor signals of the Northwest type propagate predominantly from west to east along the latitudinal 40°N, whereas those of the Southeast type occur at higher latitudes, with anomalous signals originating from the north polar region and propagating in a northwesterly-southeasterly direction.
On the other hand, the Southern Himalayas type is mainly governed by localized subtropical anomalous circulation anomalies and exhibits little association with wave train activity from mid-to-high latitudes.
The identification of significant disparities in the characteristics of extreme precipitation events, along with their associated influence on circulation patterns and precursor signals on the plateau, could offer a more robust foundation for accurately predicting extreme precipitation events during the summer season in this region.
This study was led by Ding Zhiyuan, Dr. Ha Yao, and Dr. Zhong Zhong from the College of Meteorology and Oceanography at the National University of Defense Technology.
More information: Zhiyuan Ding et al, Summer extreme precipitation patterns and synoptic-scale circulation precursors over the Tibetan Plateau, Science China Earth Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s11430-023-1321-6
Journal information: Science China Earth Sciences
Provided by Science China Press