This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New discovery highlights a potential stepping stone toward antibiotic resistance
A new study shows how heteroresistance, a transient resistance common in many bacteria, can act as a precursor to the development of antibiotic resistance. According to researchers at Uppsala University, this is the first time this link has been demonstrated.
"Heteroresistance is common and we have shown that it occurs for at least 10 different classes of antibiotics. In a patient carrying heteroresistant bacteria and undergoing treatment with antibiotics, the mortality rate and risk of requiring transfer to an intensive care unit are higher compared to susceptible bacteria.
"Therefore, if heteroresistance is a stepping stone towards resistance, we need to have much better control of its occurrence and effects," explains Dan I. Andersson, Professor of Medical Bacteriology at Uppsala University and lead researcher behind the study.
Heteroresistance is common in many disease-causing bacteria and can lead to reduced efficacy of antibiotic treatment. This particular type of antibiotic resistance means that the majority of bacteria in a population are susceptible to antibiotics, but there is also a small resistant subgroup that can grow under antibiotic treatment. These resistant bacteria carry more resistance gene copies than the others, which also results in slower growth.
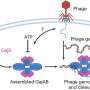
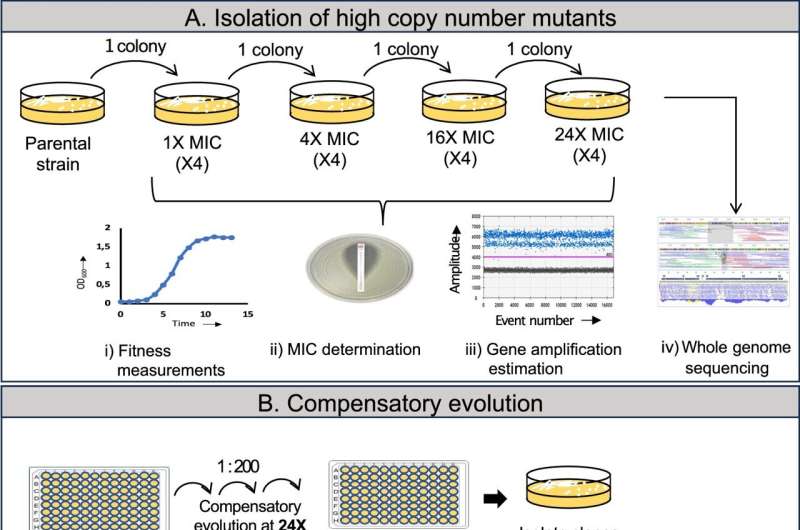
In a comprehensive study published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers at Uppsala University showed in laboratory studies that bacteria can acquire new resistance mutations that restore faster growth. In this way, heteroresistance can act as a springboard and facilitate the evolution towards stable antibiotic resistance.
"It is possible that we are wrong, but we have observed the process in the laboratory and there is no reason to believe that it would not also occur in a patient or an animal. This is an important finding in terms of understanding how bacteria become resistant to antibiotics," notes Andersson.
He believes that this discovery will lead to more clinical studies and increased diagnostics of heteroresistance in microbiological laboratories. Within health care, it is important to continue to be restrictive with antibiotics to prevent resistance.
"Antibiotics should be used in a smart way, at the right time and not unnecessarily, to prolong the lifetime of our existing antibiotics and to give us time to develop new ones," says Andersson.
More information: Ankita Pal et al, Bacteria can compensate the fitness costs of amplified resistance genes via a bypass mechanism, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46571-7
Provided by Uppsala University