This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
proofread
One easy way to fight antibiotic resistance? Good hand hygiene
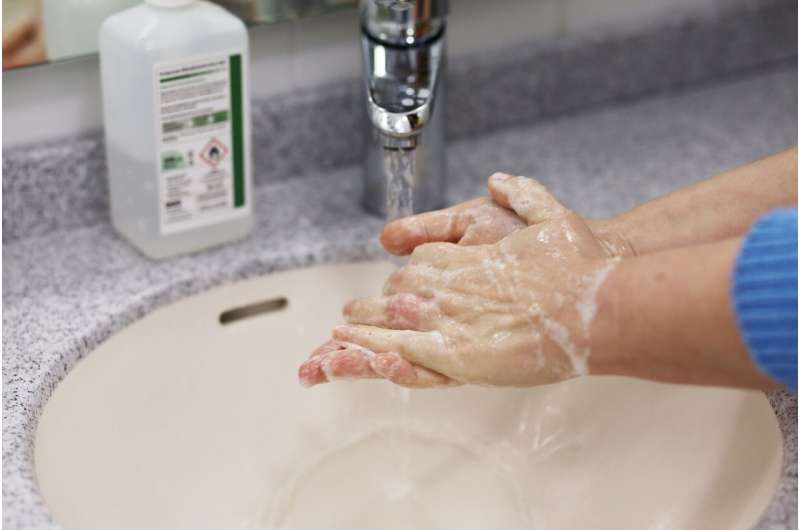

Can washing your hands help stop the evolution of antibiotic resistance? Mathematically, it's possible.
Antibiotics save lives by killing bacteria that cause infections. But antibiotics don't just kill infection-causing bacteria or stay in the area of the body where the infection is occurring. Instead, antibiotics spread across the body and inhibit or kill any sensitive bacteria they encounter.
While bacteria that are more sensitive to the antibiotics are killed off, those that are able to survive will continue to reproduce with less competition. This results in increasing abundance of resistant bacteria that can undermine the effectiveness of the antibiotic.
I am a researcher who studies the evolution of antibiotic resistance. During my medical training, I was taught about the importance of hospital hygiene practices like hand-disinfection. It is well established that good hygiene can help prevent transmission of harmful bacteria from other people or from the environment. I came to wonder how hygiene affects the evolution of antibiotic resistance.
So I teamed up with my colleagues Magnus Aspenberg, Sara Maad Sasane, Fredrik Nilsson and Sam Brown, experts in mathematics, statistics and microbial evolution, to answer this question.
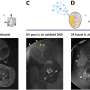
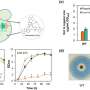
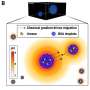
We built a mathematical model of antibiotic resistance evolution. In this model, resistant and sensitive bacteria compete in the microbial communities living in patients and transmit from one patient to another. We studied the effects of two parameters: hygiene (or use of an alcohol-based hand rub), which limits how much bacteria spreads between patients, and antibiotic use, which selects for resistant bacteria by killing sensitive ones.
We found that hygiene and antibiotic use interact. Antibiotic use had less of an effect on the evolution of antibacterial resistance as hygiene levels increased. This is because evolution toward resistance depends on variation in bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics. By affecting the distribution of resistant and sensitive bacterial strains across patients, hygiene limits the bacterial diversity needed to evolve resistance.
Research on the evolution of antimicrobial resistance has focused more on evolutionary selection than hygiene. Most studies investigate, for example, whether a high or a low dose of a drug is better to prevent resistance. Incorporating hygiene and other interventions into research on antibiotic resistance could help build a more comprehensive understanding of how bacteria evolve to become resistant.
The role of good hygiene in preventing illness is already well accepted in practice. Our findings underscore its importance by highlighting the role it plays in the evolutionary process of bacterial resistance.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()