This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
New superconducting material discovered in transition-metal dichalcogenides materials
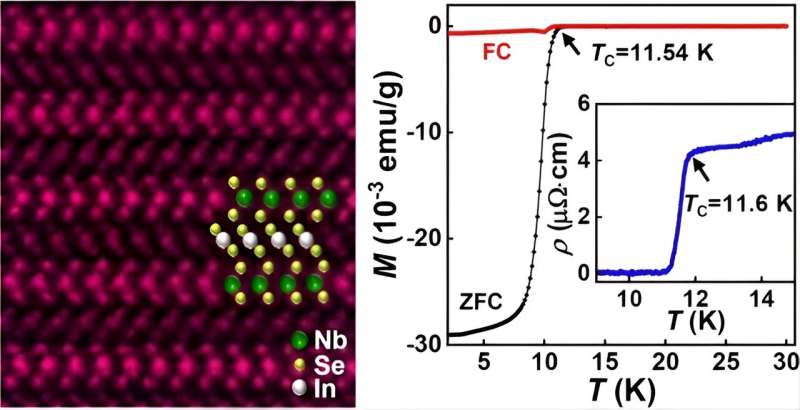
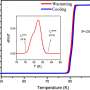
With the support of electrical transport and magnetic measurement systems of Steady High Magnetic Field Facility (SHMFF), a research team from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), discovered a new superconducting material called (InSe2)xNbSe2, which possesses a unique lattice structure. The superconducting transition temperature of this material reaches 11.6 K, making it the transition metal sulfide superconductor with the highest transition temperature under ambient pressure.
The results were published in Journal of the American Chemical Society.
TMD materials have received lots of attention due to their numerous applications in the fields of catalysis, energy storage, and integrated circuits. However, the relatively low superconducting transition temperatures of TMD superconductors have limited their potential use.
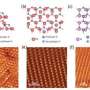
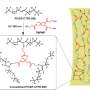
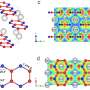
In this study, scientists successfully fabricated a new superconducting material with the chemical formula (InSe2)xNbSe2. Unlike the conventional conditions where isolated atoms are inserted into the van de Waals gaps of low dimensional materials, in (InSe2)xNbSe2 the intercalated indium atoms were found to form InSe2-bonded chains.
"This material has a very high transition temperature among all transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) superconductors," said Prof. Zhang Changjin, who led the team, "and it exhibits an impressive critical current density."
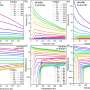
The superconducting transition temperature of the (InSe2)0.12NbSe2 sample could be as high as 11.6 K at ambient pressure, which is 60% higher than that of pristine NbSe2.
Furthermore, the (InSe2)xNbSe2 superconductor exhibits large critical current density of 8x105 A/cm2, which is also the highest among all TMD superconductors. The critical current density is comparable with high-temperature superconductors such as cuprate and iron-based compounds, demonstrating its good application prospects.
This discovery opens up new possibilities for advancing superconductivity research and developing high-temperature superconductors with improved performance, according to the team.
More information: Rui Niu et al, Enhanced Superconductivity and Critical Current Density Due to the Interaction of InSe2 Bonded Layer in (InSe2)0.12NbSe2, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c09756
Journal information: Journal of the American Chemical Society
Provided by Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences