This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New report outlines gaps in preparing young people to respond to tech-facilitated sexual harm
Schools and teachers play a critical role in equipping students with the skills to understand, respond to, and prevent sexual violence in safe and healthy ways. As the lines between the digital and physical world continue to blur, young people are reporting that these harms are increasingly being perpetrated online through actions like the sending of unwanted sexually explicit messages, cyber flashing, cyberstalking, or sharing intimate images without consent.
A group of researchers, led by Sociology professor Kaitlynn Mendes, explored how the curriculum in Canada addresses these forms of "technology-facilitated sexual violence" and found there is significant room for improvement to make young people feel empowered to both prevent and adequately respond to these actions.
This research is part of a five-year project called Digitally Informed Youth (DIY): Digital Safety, which aims to empower young people and provide them with tailored resources so they can have safe and enjoyable interactions online and offline.
"This is why we are doing this research—to show that these are topics that aren't being talked about or if they are being talked about, they often use victim-blaming language," said Mendes. "There is an urgent need to address this because we know young people are not asking for help when they're in trouble; they are trying to solve these things on their own. Then we see the worst-case scenario consequences where they take their own lives."
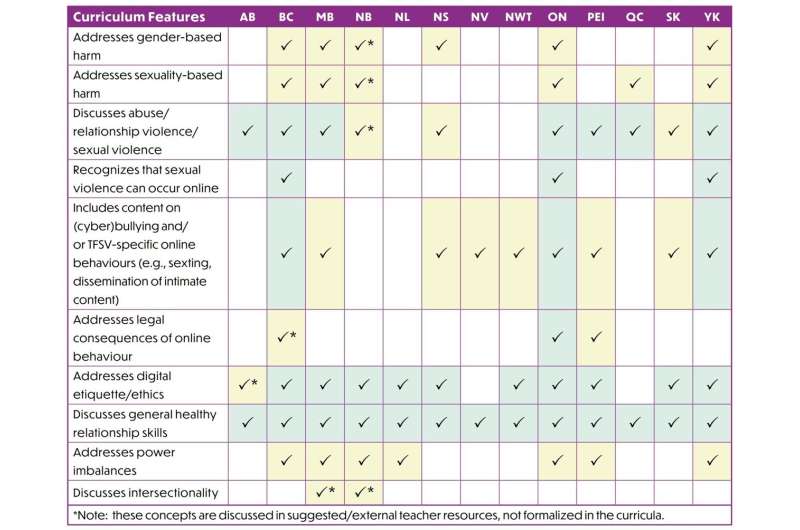
A report co-authored by Mendes and collaborators at Dalhousie, McGill, and Saint Mary's University and funded by SSHRC found topics related to tech-facilitated sexual violence are addressed inconsistently across the country and are included mainly through anti-bullying legislation.
The researchers point out that addressing these behaviors under the umbrella of bullying and labeling them as "cyberbullying" diminishes the harm experienced by young people. It also doesn't address the resources and legal support that may be available to young people related to sexual violence.
The report also shows that while most provinces and territories address general healthy relationships and relationship- and sexual violence as part of the high school curriculum, few recognize that sexual violence can occur online or via digital technologies.
Mendes says education on tech-facilitated sexual violence often takes a risk-based approach, which suggests technology is inherently dangerous and can stigmatize students or make them feel ashamed when they experience these harms online.
Recommendations for improvement
A key part of the report is not just addressing the gaps in teaching but also offering recommendations for improvement.
The researchers' five recommendations are:
- Include specific references to various forms of tech-facilitated sexual violence to help young people understand a broad range of harmful behaviors and available resources.
- Do not treat online harms as separate and distinct from young people's full lived experiences.
- Refrain from taking a risk-based approach to technology. Instead of scaring or shaming students about dangers related to their use of technology, educators should encourage students to identify and address harms as they arise.
- Inform students about their technology-related rights and responsibilities and let them know what resources and supports are available to them when they need help.
- Specifically address the gender-based and sexuality-based nature of these tech-facilitated harms, including information on how power, intersectionality, and forms of oppression factor in.
"A fundamental part of our project is not just saying here's the problem, but also trying to find solutions," said Mendes.
As a follow-up to the report, the research team is now in the process of conducting focus groups with young people across the country to understand their lived experience with tech-facilitated sexual violence.
"We want to be able to go back to the provinces and territories and help them understand what young people are experiencing, so we can inform policymakers on where the gaps are and develop resources on best practices going forward."
More information: Report: Technology-facilitated sexual violence in Canadian educational curricula, policies, and legislation
Provided by University of Western Ontario