This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Sperm's secret voltage switch: Scientists unlock the mystery of motility
Researchers at Stockholm University have unveiled the hidden intricacies of how sperm go from passive bystanders to dynamic swimmers. This transformation is a pivotal step in the journey to fertilization, and it hinges on the activation of a unique ion transporter. Their research has been published in Nature.
Imagine sperm as tiny adventurers on a quest to reach the ultimate treasure, the egg. They don't have a map, but they make use of something even more extraordinary: chemo-attractants. These are chemical signals released by the egg that act as siren call, directing and activating the sperm. When these signals bind to receptors on the sperm's surface, it triggers a series of events, starting their movement towards the egg. And in this intricate scenario, one key player is a protein known as "SLC9C1."
It's exclusively found in sperm cells, and it is usually not active. However, when the chemo-attractants interact with the sperm's surface, everything changes.
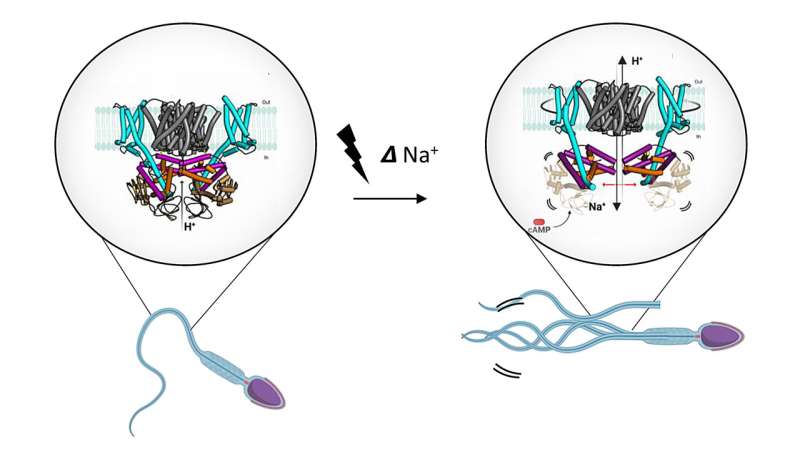
"SLC9C1 operates like a highly sophisticated exchange system. It swaps protons from inside the cell for sodium ions from the outside, temporarily creating a less acidic environment within the sperm. This change in the internal environment triggers increased sperm motility," says David Drew, Professor in Biochemistry at Stockholm University.
The activation of SLC9C1 is driven by a change in voltage that occurs when chemo-attractants attach to the sperm. To accomplish this, SLC9C1 uses a unique feature called a voltage-sensing domain (VSD). Typically, VSD domains are associated with voltage-gated ion channels. But in the case of SLC9C1, it's something truly exceptional in the realm of transporters.
Researchers, led by David Drew, have unveiled the secrets behind SLC9C1's inner workings and provides the first example of voltage-sensing domain activation of a transporter and its connection via an unusually long voltage-sensing (S4) helix.
"The VSD domain responds to the change in voltage by pushing its rodlike S4 helix inwards. This clears the way for ion exchange by SLC9C1, ultimately initiating sperm motility," says David Drew.
"Transporters work very differently than channels and, as such, the VSD is coupled to the sperm protein in a way that we have just never seen before, or even imagined. Its exciting to see how nature has done this and perhaps, in the future, we can learn from this to make synthetic proteins that can be turned-on by voltage or develop novel male contraceptives that work by blocking this protein," David Drew notes.
More information: David Drew, Structure and electromechanical coupling of a voltage-gated Na+/H+ exchanger, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06518-2. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06518-2
Journal information: Nature
Provided by Stockholm University