This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Researchers report effect of hypoxia on periosteal stem cells
A new study has shown that the interaction of miR-584-5p and RUNX2 could mediate PSC osteogenic differentiation induced by hypoxia. The work is published in the World Journal of Stem Cells.
The hypoxic environment during bone healing is important in regulating the differentiation of periosteal stem cells (PSCs) into osteoblasts or chondrocytes; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
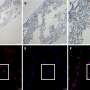
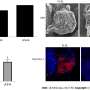
The researchers aimed to determine the effect of hypoxia on PSCs. They isolated primary mouse PSCs and stimulated them with hypoxia, and the characteristics and functional genes related to PSC osteogenic differentiation were assessed. Constructs expressing miR-584-5p and RUNX2 were established to determine PSC osteogenic differentiation.
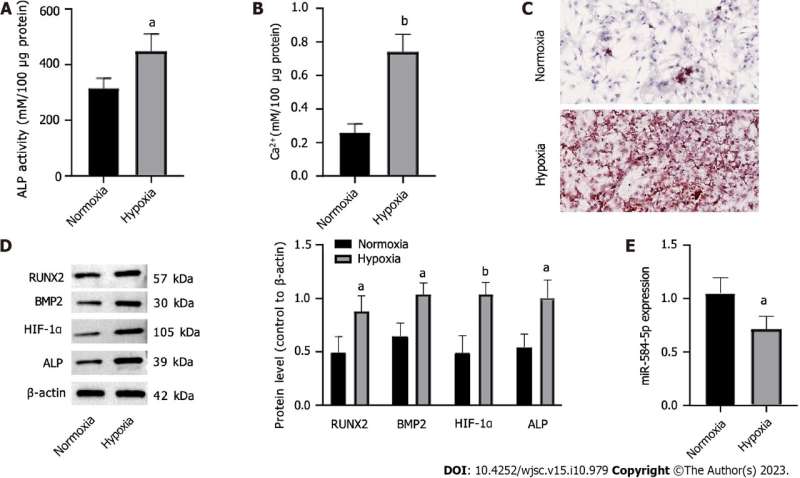
The results showed that hypoxic stimulation induced PSC osteogenic differentiation and significantly increased calcified nodules, intracellular calcium ion levels, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in PSCs. Osteogenic differentiation-related factors such as RUNX2, bone morphogenetic protein 2, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, and ALP were upregulated; in contrast, miR-584-5p was downregulated in these cells.
Furthermore, upregulation of miR-584-5p significantly inhibited RUNX2 expression and hypoxia-induced PSC osteogenic differentiation. RUNX2 was the target gene of miR-584-5p, antagonizing miR-584-5p inhibition in hypoxia-induced PSC osteogenic differentiation.
More information: Jia-Jia Lu et al, MicroRNA-584-5p/RUNX family transcription factor 2 axis mediates hypoxia-induced osteogenic differentiation of periosteal stem cells, World Journal of Stem Cells (2023). DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i10.979
Provided by World Journal of Stem Cells