This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Researchers invent a new metallization method of modified tannic acid photoresist patterning
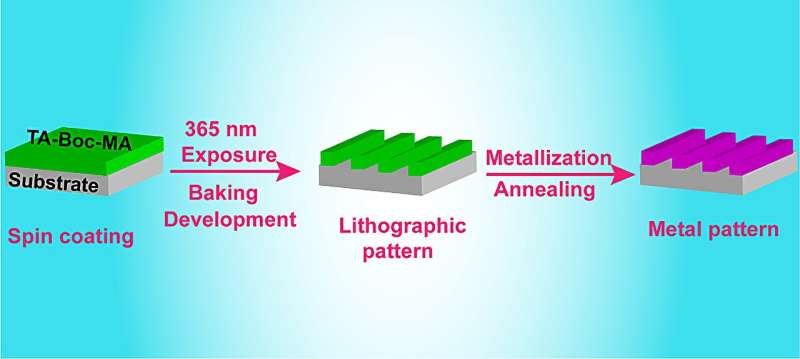
The micro/nano metal pattern formation is a key step in the assembly of various devices. However, ex situ approaches of metal patterning limited their industrial applications due to the poor stability and dispersion of metal nanoparticles. The in situ electroless deposition after lithography patterning may be a better choice for avoiding the growth and aggregation of metal particles in the polymers.
Tannic acid is rich in natural products, having an adjacent tri-hydroxyl structure, which can realize the in situ reduction of metal ions on the photoresist pattern. A team of scientists has invented a new metallization method with modified tannic acid photoresist patterns. Their work is published in the journal Industrial Chemistry & Materials.
"We aimed to build a novel photoresist and the process for the direct photoresist pattern transformation to a desired metal pattern," explains Wenbing Kang, a professor at Shandong University. The metallization method is different from normal metal patterning using a metal film and photoresist pattern using etching and resist removal process. It could be a good choice for metal pattern formation on various substrates and also possible for flexible devices.
Surface patterning techniques for micro-nano structures are key to the rapid development of science and technology. However, metallization of the pattern is a key step in assembling various devices. In ex situ approaches of metal patterning, researchers usually use "metal ink" with the assistance of an inject printer or soft-lithography method to form patterns on different substrates.
However, their industrial applications are restricted by poor performance owing to poor stability and dispersity of metal nanoparticles and lower resolution caused by the coffee ring effect and surface tension.
With the increasing requirements for high resolution metal patterning, pioneers have developed a direct laser writing technique by combining in situ approaches with direct lithography to realize in situ dispersion of metal nanoparticles in polymers.
However, the local hyperthermal effects of the laser by direct photoradiation on the metal precursors in polymers can lead to the uncontrollability of metal growth and aggregation of particles, resulting in the irreversible loss of photoelectric properties. Hence, in situ electroless deposition after lithography patterning could be a better choice for avoiding the growth and aggregation of metal particles in the polymers.
Phenolic hydroxyl groups play a rather important role in in situ electroless deposition due to their strong interactions with various metal ions and their reducing powder. Tannic acid is rich in natural products, having an adjacent tri-hydroxyl structure, which greatly improves its ability to reduce metal ions. However, tannic acid often needs to be modified by some hydrophobic groups to improve the resistance in an alkaline developer and solubility in organic solvent for better photoresist performance.
Despite the fact that modified tannic acid has been applied in photoresist patterning, an in situ metallization method based on a tannic acid photoresist pattern has not been seen yet.
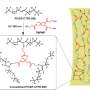
The research team was able to successfully design a chemical amplified photoresist system using tannic acid protection with BOC and methacryloyl groups and the resist process with dual exposure to make sure the resist pattern to metal pattern is successful. They used the modified tannic acid to blend to photoresist with a photoacid generator (PAG103) for the lithographic pattern by spin-coating, exposure with a mask, baking and develop.
Then they invented the second exposure and baking to remove the protection groups in the resist film to regenerate the phenolic hydroxyl groups for sufficient reduction powder. Finally, the Ag pattern could be in situ constructed by metallization of the lithographic pattern through the reduction of Ag+ to Ag nanoparticles utilizing the high reduction power of phenolic groups.
The regeneration of the phenolic hydroxyl group in the second exposure and baking procedure plays an important role in the formation of the Ag pattern. The Ag film had excellent conductivity and the square resistance was about 1 Ω sq−1.
Looking ahead, the research team hopes that their work might provide insights into the method and formation process of Ag pattern based on modified tannic acid photoresist patterning. "We are working on to the application of this strategy in the formation of other metal films or metal patterns. This process has potential applications in devices assembly," said Kang.
More information: Zicheng Tang et al, A new metallization method of modified tannic acid photoresist patterning, Industrial Chemistry & Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D3IM00066D
Provided by Industrial Chemistry & Materials