This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Thermally induced orderly alignment of porphyrin photoactive motifs in metal-organic frameworks
Professor Shi Weiqun's group from the Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has made progress in the application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) in the field of photocatalytic CO2 reduction. The study was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society.
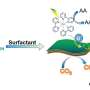
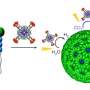
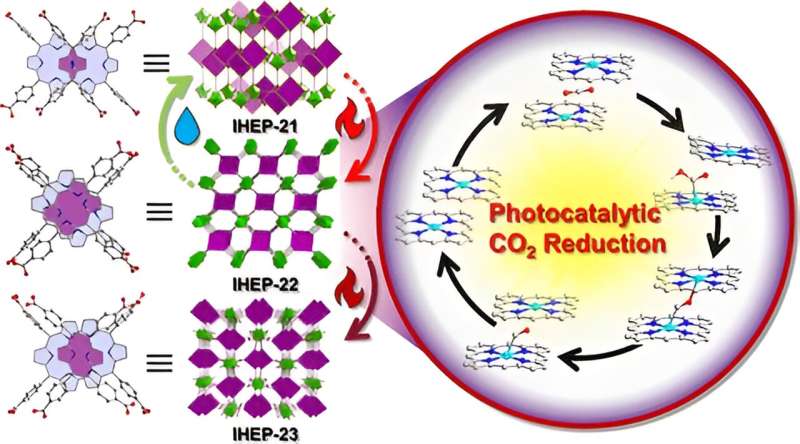
The researchers constructed the MOF material IHEP-21 with the actinide metal thorium as the node and the functional organic ligand porphyrin, and proposed to utilize a thermally induced strategy to obtain the MOF materials IHEP-22 and IHEP-23 via a two-step single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation. The large ionic radius and high coordination number of thorium give IHEP-21 more structural variability, which is conducive to the thermally induced multi-step crystal transformation process of actinide-porphyrin MOFs.
The structural analysis showed that the extent of stacking of porphyrin molecules in the materials changed after a two-step structural transformation, which greatly affected the photoelectric properties and photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity of the materials.
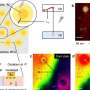
The photoelectrochemical characterization and theoretical calculation showed that the electron transport pathway formed between the porphyrin molecules inhibits the recombination of photogenerated carriers, thus realizing efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction.
This work provides a new method for regulating the separation and migration of carriers in photocatalysts, which is helpful in guiding the design and synthesis of photocatalysts with excellent performance for the production of solar fuels.
More information: Zhi-Wei Huang et al, Thermally Induced Orderly Alignment of Porphyrin Photoactive Motifs in Metal–Organic Frameworks for Boosting Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c07047
Journal information: Journal of the American Chemical Society
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences