This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Sugars affect brain 'plasticity,' helping with learning, memory, recovery
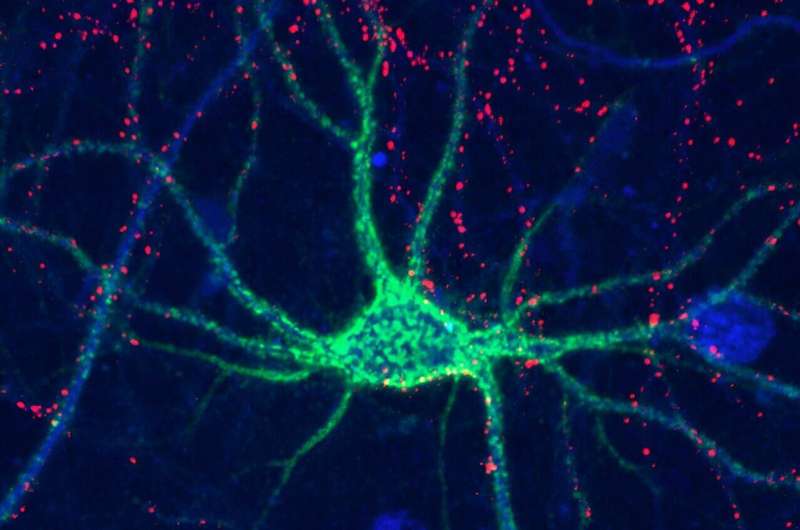
Can you recognize someone you haven't seen in years, but forget what you had for breakfast yesterday? Our brains constantly rearrange their circuitry to remember familiar faces or learn new skills, but the molecular basis of this process isn't well understood. Today, scientists report that sulfate groups on complex sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) affect "plasticity" in the brains of mice. Determining how GAGs function could help us understand how memory and learning work in humans, and provide ways to repair neural connectivity after injuries.
The researchers will present their results today at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
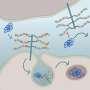
The sugars that sweeten fruits, candies or cakes are actually just a few simple varieties of the many types of sugars that exist. When strung together, they can make a wide array of complex sugars. GAGs are formed by then attaching other chemical structures, including sulfate groups.
"If we study the chemistry of GAGs in the brain, we can learn about brain plasticity and hopefully, in the future, use this information to restore or enhance neural connections involved in memory," says Linda Hsieh-Wilson, Ph.D., the project's principal investigator presenting the research at the meeting.
"These sugars regulate numerous proteins, and their structures change during development and with disease," she explains. Hsieh-Wilson is at the California Institute of Technology.
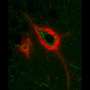
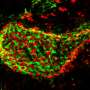
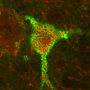
In the brain, the most common GAG form is chondroitin sulfate, which is found throughout the extracellular matrix surrounding the brain's many cells. Chondroitin sulfate can also form structures known as "perineuronal nets," which wrap around individual neurons and stabilize the synaptic connections between them.
One way a GAG's function can be changed is through sulfation motifs, or patterns of sulfate groups tacked onto the sugar chains. Hsieh-Wilson's team is interested in how those sulfation patterns become altered, and how they might regulate biological processes such as neuroplasticity and social memory. This could also one day allow researchers to modulate these functions as a potential treatment for central nervous system injuries, neurodegenerative diseases or psychiatric disorders.
When the team deleted the Chst11 gene responsible for forming two major sulfation patterns on chondroitin sulfate in mice, defects formed in their perineuronal nets. However, the number of nets actually increased in the absence of the sulfation motifs, changing the types of synaptic connections between neurons. In addition, the mice were unable to recognize mice to whom they had previously been introduced, which suggests that these patterns affect social memory.
Interestingly, these nets might be more dynamic than once thought—they could be playing a role in both childhood and adulthood. When the researchers targeted Chst11 specifically in the brains of adult mice, they found the same effects on perineuronal nets and social memory. "That result suggests that it may be possible to manipulate these nets during adolescence or adulthood to potentially rewire or strengthen certain synaptic connections," says Hsieh-Wilson.
In other recent experiments, the team wanted to understand how GAGs and their sulfation patterns could affect axon regeneration, or the ability of neurons to rebuild themselves after injury. The researchers are now working to identify protein receptors that bind particular sulfation motifs. So far, they have found that specific motifs cause these receptors to cluster together at the cell's surface and inhibit regeneration. This process could be blocked to create tools or treatments to promote axon regeneration. Having more insight about this process could someday help repair damage caused by certain neurodegenerative diseases or strokes, Hsieh-Wilson says.
More information: Harnessing chemistry to understand the roles of glycans in neuroplasticity, ACS Fall 2023.
Provided by American Chemical Society