This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers produce polymers from ballbot-type carbenes for the first time
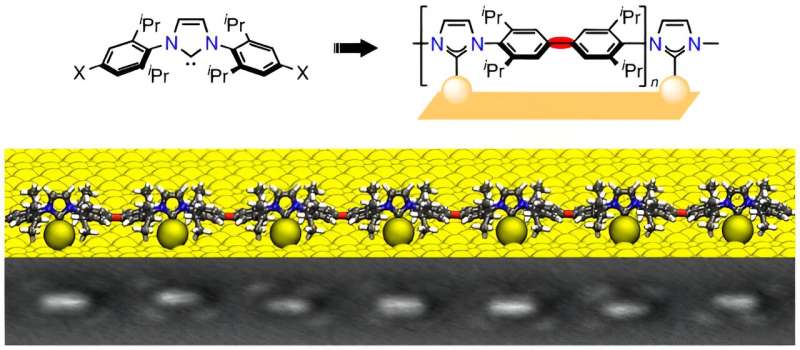
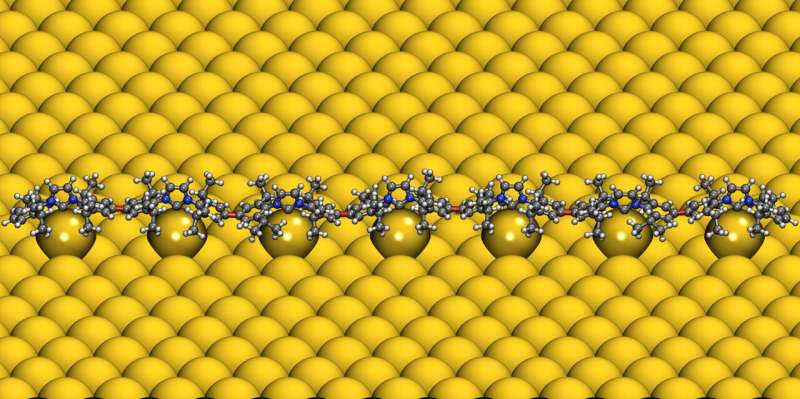
N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are small, reactive ring molecules that bond well with metallic surfaces, and which over the past few years have attracted a great deal of interest in the field of the stable chemical modification of metallic surfaces. One property—discovered at the University of Münster in Germany a few years ago—is the ability that certain NHC derivatives have, not only to anchor themselves to individual metal atoms, but also to completely extract an individual atom from the surface. Having bonded with these so-called adatoms, the NHCs glide freely over the surface—like a ballbot, i.e., a robot that moves on a sphere.
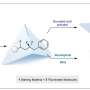
Using such "ballbot molecules," and working together with Chinese researchers, the Münster physicists and chemists have succeeded for the first time in making the halogenated NHCs produce long-chain mobile polymers—chains of molecules—on metallic surfaces. Details of the work have been published in the journal Nature Chemistry.
The mobility of the ballbot-type NHCs opens up new possibilities, for example self-assembly into highly ordered domains from this type of molecule, up to cooperative, swarm-type behavior on the part of the NHCs in autonomously converting certain metallic surfaces into a different highly-ordered structure without any external influence such as light or electrons.
"Over and above the self-organization, these ballbot polymers hold great promise for new applications in nanoelectronics, surface functionalization and catalysis," says Prof. Harald Fuchs, Senior Professor at Münster University's Institute of Physics and Scientific Director of the Center for NanoTechnology (CeNTech) at Münster.
NHCs can be be easily modified in the nitrogen (N) groups of the five-fold heterocyclic body of the molecules. As a result, this makes it possible not only to influence the electronic interaction between the carbenes and the atoms of a metallic surface—for example, gold—but also to control the alignment of the carbenes vertically or parallel to a surface.
One special feature of the halogenated NHCs used, which were developed at the Institute of Organic Chemistry at the University of Münster, is their ability to spontaneously form adatoms on noble metals and the mobility which arises as a result. This is a prerequisite for their coming together and for the reaction with other reactive systems on the surface.
"A decisive factor in the success of the experiments was the balance between the chemical reactivity of the monomeric structural units and their mobility," says lead author Prof. Jindong Ren, formerly a postdoctoral researcher in Prof. Harald Fuchs's group and now a principal investigator (PI) and group leader at the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST) of China.
On the one hand, the monomers can move easily on the surface due to their ballbot property; on the other hand, the contact time which the parties to the reaction have needs to be of a sufficient length to make the reaction happen. This occurs above all through the molecular structure and a suitable temperature setting during the experiment.
Controlling the chemical reactions and providing evidence for the desired reaction products in the field of precision chemistry for surfaces requires highly specialized preparative and analytical experiments that allow molecular interactions on surfaces and individual reaction steps at a submolecular scale to be observed.
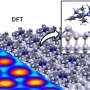
For this purpose, the researchers at CeNTech, NCNST and at Beijing National Center for Condensed Matter Physics and Institute of Physics employed scanning probe microscopy methods (STM and nc-AFM), as well as photoemission spectroscopy, to clarify the chemical bonding taking place and to provide evidence of the ballbot structures.
The experimental results were complemented by elaborate computer simulations at the Institute of Solid State Theory at Münster University, based on quantum mechanics approaches and reactive force fields. In this way, the team confirmed the experimental results and quantified the electronic and structural properties of the ballbot polymers.
Precision chemistry on surfaces has now evolved into a separate area of chemistry. Unlike in traditional chemistry in a test tube or the gas phase, this particular branch of chemistry requires ultra-high vacuum conditions, and often, temperatures as low as minus 268 degrees Celsius in order to avoid any unintentional contamination, as well as to enable the observation of chemical (intermediary) steps at the molecular level.
Solid surfaces—usually crystalline—serve as the platform (substrate) for the reaction and they can also support the reaction catalytically. Nano-structured surfaces, such as those used in the work described above, make it possible to control not only the alignment, but also a selective geometric arrangement of the reaction products or of the resultant polymers.
More information: Jindong Ren et al, On-surface synthesis of ballbot-type N-heterocyclic carbene polymers, Nature Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41557-023-01310-1
Journal information: Nature Chemistry
Provided by University of Münster